How to Login to WordPress Admin (Beginner-Friendly Tutorial)
Great job on getting your website up and running! Choosing WordPress was definitely the right thing to do, as it is the platform that powers more than 40% of the websites worldwide. This widely used content management system (CMS) is well-known for its configurability, rich features, and simple interface, thus it suits perfectly any kind of a website from a personal blog to an elaborate e-commerce site. It’s actually the best way to show off your stuff.
On the other hand, you could be staring at your freshly published home page and wondering, “How do I even start to customize this?” Feeling somewhat overwhelmed is totally fine in this situation.
It’s okay, you have support! The feeling of confusion has been experienced by all WordPress users, be it advanced developers or first-time website owners, and that’s the only common thing they have. You have to get to the “backend” of your site, which is the WordPress admin dashboard, before you can post your first insightful blog, upload attractive photos, or totally revamp your site with a new theme. Consider this as the control panel, where you run the operations of your site.
So, you have to figure out how to get into the WordPress admin area.
This manual is designed just for beginners like you. We will take you the whole way step by step, letting you know of each stage. We will also provide fixes for the trouble spots you may encounter and give away some useful pro-tips like how to keep your login safe and stop unwanted visitors from accessing your site.
Lets get you into the driver’s seat of your new website and start building your online presence. You will be creating and customizing before you know it!
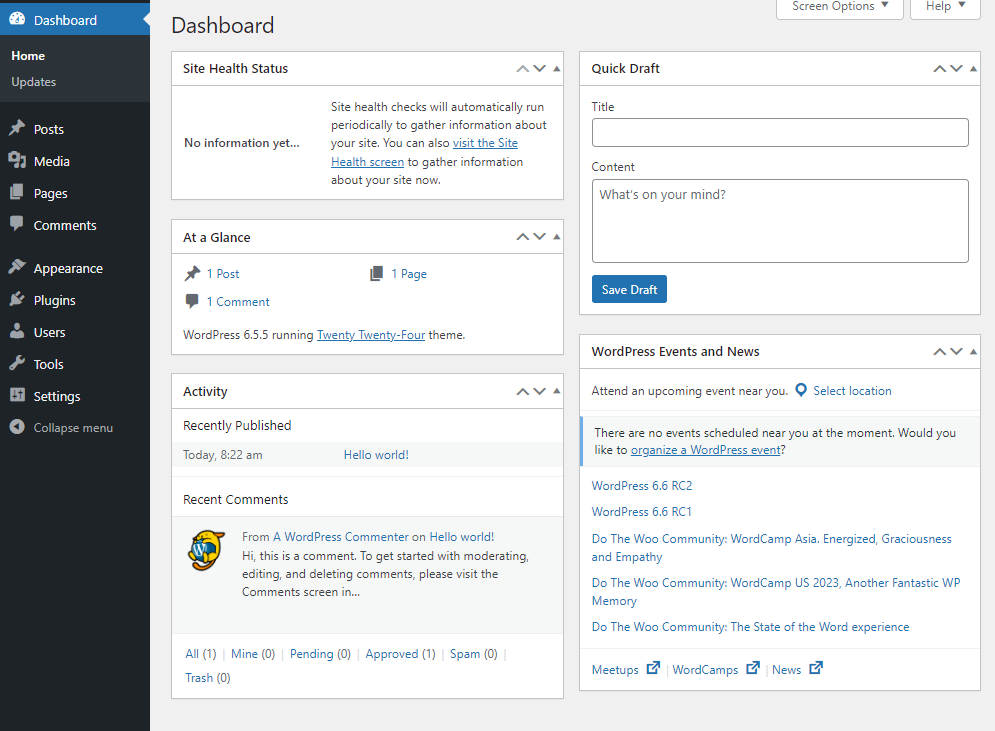
What Is the WordPress Admin Dashboard?
Here is your text cleanly formatted, rewritten in a natural human tone, without adding or removing anything, and keeping everything intact as requested:
Before we get into logging in, it’s essential to figure out exactly what kind of access you will have. Knowing the difference between the public face of your website and its inner administrative part is a must if you want to be in charge of your online presence properly.
What you see when you type in the address of your website (e.g., www.getsocialguide.com) is the front-end. This is the part of the site that is available to users — the content and design that visitors get to see and interact with. In a way, it’s the public display of your hard work, the shop window, the welcome mat. Its purpose is to be attractive, useful, and visually engaging, aimed at gathering and keeping the audience.
The WordPress Admin Dashboard, also known as the backend or administrative area, is the command center of your site. It’s the private area behind the public facade, accessible only to those with a unique username and password. This secure place is where you build, organize, and manage everything that keeps your website running.
You can think of it like this: your website’s front-end is the restaurant dining area — beautifully decorated rooms where customers enjoy their meals, music plays softly, and the atmosphere draws people in. The Admin Dashboard is the kitchen — where you (the chef) prepare the meals (content), manage ingredients (media), and oversee daily operations. It’s also where business tasks happen, like handling employees, updating the menu, and taking care of finances.
Once you’ve logged into the dashboard, you unlock a powerful range of tools and features. You can:
Create and Manage Content:
This is the core of your website. You can write and publish blog posts to keep readers engaged. You can also build essential pages like “About Us,” “Contact,” or “Services” to describe your business. Plus, you can add photos, videos, and other media to make your content more appealing.
Change the Design:
You can shape how your site looks and feels. Activate and test different themes, each offering a different visual style. Then customize those themes with your own colors, fonts, and layout choices so your site fits your brand perfectly.
Add Functionality:
Plugins let your website do more. These small add-ons introduce specific features. A contact form plugin lets visitors send you messages easily. SEO plugins guide you in optimizing your content for search engines. E-commerce plugins can turn your site into a fully functioning online store for selling products or services.
Manage Users:
If you’re working with a team, you can add contributors and assign roles to control what each person can access. For example, writers can be given the “Author” role so they can create and edit their own posts. Someone with full authority, like an “Administrator,” can manage the entire site. Authors can publish or edit posts but cannot change other settings on the website.
Configure Settings:
Here, you fine-tune how your site works. Set your site title, control whether visitors can leave comments, and choose how your URLs (permalinks) appear so search engines can easily understand them. This is where ideas turn into a polished, functional web presence.
Now that the groundwork is clear, it’s time to step into that important kitchen.
Step 1: Accessing the Login Page
The primary step in learning how to login to WordPress admin is figuring out where the login page is. WordPress has default URL structures that virtually all installations utilize, which makes this very simple.
Finding your login page entails adding a specific “slug” to the end of your site address in the browser’s address bar.
There are two default URLs which will work in almost all cases:
example.com/wp-admin
example.com/wp-login.php
(Note: Replace “[suspicious link removed]” with your actual website address.)
For instance, if your website is awesomebaking.com, you would enter awesomebaking.com/wp-admin in your browser.
[Screenshot of a browser address bar showing a domain followed by /wp-admin, highlighting the URL structure.]
By typing in this URL, you will be able to see the login screen as WordPress will perform the redirect automatically.
Important Variations
The regular URLs function almost all the time, but there may be a few cases where your login URL could be quite different:
Installed in a Subdirectory:
Suppose your main website is made with HTML and you have a WordPress blog installed in a folder named “/blog/. Your login URL will then be yourdomain.com/blog/wp-admin.
Custom Login URLs:
To make it more secure, some WordPress hosting providers or security plugins might change the default path of /wp-admin to something different to make it hard for the hackers to locate the login page quickly. First of all, if the regular URLs are not working, then check the welcome email that you received from your hosting provider at the time of setting up your account.
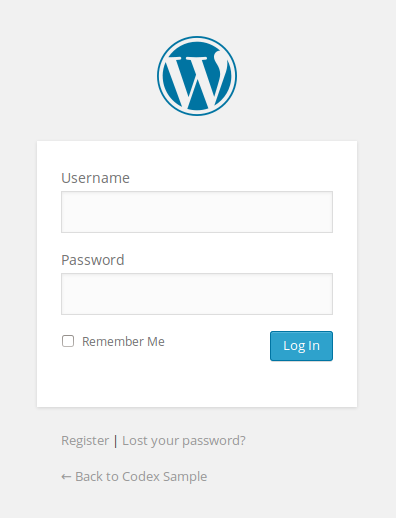
Step 2: Enter Your Username and Password
Once you successfully navigate to the URL, you will see the classic WordPress login screen. It usually features the WordPress logo at the top, followed by two fields.

Here, you need to enter the credentials you created during the WordPress installation process.
- Username or Email Address: You can use either the username you chose or the email address associated with that administrator account. Using the email address is often easier to remember.
- Password: Enter your secure password.
The “Remember Me” Checkbox
Just below the password input area, there is a little checkbox with the label “Remember Me.”
If you tick this box before hitting the “Log In” button, WordPress will set a cookie in your browser that keeps you logged in for 14 days unless you log out manually. If you don’t check it, you will usually be logged out when you close your browser or after a certain period of inactivity (normally 48 hours).
Security Warning: Only check “Remember Me” if you are on your own private, secure computer. Never use this option on a public computer (e.g., at a library or internet cafe) or a shared device, as the next person to use that computer will be able to access your website’s backend without a password.
After entering your username and password, click on the blue Log In button. If everything is right, you will be redirected to your WordPress Dashboard.
Step 3: Common Login Issues and Solutions
There are occasions when you might be following the instructions one after another to figure out how to log in to the WordPress admin and still things might not be working as they should. It is not necessary to be anxious — problems with login are very frequent, and a great number of them can be solved in a simple manner.
Firstly, here are the three most common problems that beginners may encounter and the methods to overcome them.
Forgot Password
This is the most frequent issue. We each have an overload of passwords to remember.
If you do not remember your password or WordPress informs you that it is wrong:
- Look at the screen below the login box, which is in white color.
- Click on the link that says “Lost your password?”
- A new page will request a username or email. You can type in either one.
- Click on the “Get New Password” button.
WordPress will shortly send a message to the email address associated with your account. This message will include a unique link. By clicking that link, you can set a new password.
(If the email is not in your inbox, please check your Spam or Junk folder.)
For power users, in case the email reset is not functioning, there are methods to change the password through the database (phpMyAdmin) of your hosting control panel. Nevertheless, the email method is generally sufficient for novices.
URL Errors
If you type /wp-admin and get a “404 Page Not Found” error or a blank white screen, double-check the following:
Domain Typo:
Make sure you didn’t accidentally mistype your web address. It happens to all of us.
HTTP or HTTPS:
If your site uses an SSL certificate (and it definitely should), ensure that you are typing https:// at the beginning of your URL instead of http://.
Browser Cache:
Sometimes your browser “keeps” an old version of a page that didn’t load correctly. Clearing your browser’s cache and cookies or opening the login page in Incognito/Private mode can help you check if the issue is caused by caching. If the login page opens normally in Private mode, then the cache was the cause.
H3: Security Restrictions / IP Block
There are times when just because your site is blocking you for security reasons you are not able to log in.
If you (or someone) have tried to guess your password and, after the wrong one was entered too many times, security plugins (like Wordfence or iThemes Security) or the firewall of your hosting may block your IP address for a certain time.
It is actually quite good-things that your security measures are there and working to stop hackers from forcibly getting access by brute force.
If you consider yourself blocked:
Let the block be lifted: In most cases these blocks are temporary (for instance, 30 minutes). Wait some time and then try again with the right password but slowly.
Use a different connection: Try to log in on your phone but use cellular data instead of your home Wi-Fi. In this way, a different IP address will be used. If by using your phone you can log in, then the conclusion is that your home IP was blocked.
Contact your host: When you are completely locked out, the only thing you can do is to contact the support of your web hosting. They can check their server firewalls and remove your IP address block.
Tips to Secure Your WordPress Admin Login
Knowing how to get to the WordPress admin login is one thing but ensuring that no one else uses that knowledge to log in is a completely different matter.
Being the most widely used platform for building websites, WordPress is the number one target for hackers. As a matter of fact, hackers usually attempt to break into your site through the login page at first. Here are four critical tips that could help keep them out.
Tips to Secure Your WordPress Admin Login
Protecting your login page is critical to keeping your entire site safe. Here are essential security best practices:
- Use Strong, Unique Passwords: Never use simple passwords. Create long, complex passwords or use a password manager to generate and store them. Avoid using “admin” as a username.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): This adds a second verification step, like a code from your phone, making it much harder for hackers to access your account even if they have your password.
- Limit Login Attempts: Use a security plugin to block an IP address after a few failed login attempts. This stops “brute force” attacks where bots try thousands of password combinations.
- Change the Default Login URL: Plugins like WPS Hide Login let you change your login page from /wp-admin to something unique like /my-secret-entry, which stops a large amount of automated bot traffic.
- Keep Everything Updated: Always run the latest versions of WordPress core, themes, and plugins. Updates often patch security vulnerabilities that hackers exploit.
- Install a Web Application Firewall (WAF): A firewall like Sucuri or Cloudflare blocks malicious traffic and hacking attempts before they even reach your login page.
- Use SSL/HTTPS: Ensure your site uses HTTPS. This encrypts data between the user and your server, protecting login credentials from being intercepted. Many hosts now offer free SSL certificates.
Conclusion
The ability to log into your WordPress admin is a straightforward operation but holds great significance. Generally, you just need to append /wp-admin to your website’s address, type in your login details, and you are free to manage your site. If anything goes wrong, carefully diagnose the problem by following the steps you figured out above. For instance, you can start with resetting your password and checking the browser before proceeding with more elaborate fixes like FTP.
Accessibility to your WordPress admin dashboard is not a big deal if you know the exact URL and have the login details. Being aware of typical login issues, taking necessary precaution for security, and signing in with correct login details will not only grant you access to the admin but also keep the site safe from hackers.
First and foremost, after getting access to the admin panel, focus on securing your website. The use of strategies such as strong passwords, the 2FA feature, and the installation of a trustworthy security plugin will help you avoid troubles later on and keep your digital assets intact.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How do I find my WordPress login URL?
Your WordPress login URL by default is the domain of your site together with /wp-admin or /wp-login.php (for example, www.yourwebsite.com/wp-admin). In case it doesn’t operate, it might be that your security plugin or the administrator of your site has changed the URL.
What to do if I forget my password?
On the login page, hit the “Lost your password?” option. Then you should provide either your username or the e-mail address to get an URL for reset. If it doesn’t work, you probably have to set a new one via your database in phpMyAdmin.
Can I limit login attempts to secure my admin?
Indeed, it is possible and highly advised practice. A security plugin such as Sucuri, Wordfence, or iThemes Security can be used to limit the number of failed attempts to login from a certain IP address and thus be able to stop brute force attacks.






