Your Complete Beginner’s Guide to Mastering SAS Programming
In a world driven by data, the ability to transform raw numbers into actionable insights is a superpower. If you’re a statistician, analyst, or aspiring data scientist looking to make sense of massive datasets, SAS (Statistical Analysis System) is a tool you need to know. This guide is designed for absolute beginners. We’ll walk you through everything—from what SAS is and why it’s dominant in industries like finance and healthcare, to writing your first programs and planning your certification path.
Why Learn SAS? Power and Stability in the Analytics World
SAS was established in the 1970s and has grown to become a global leader in analytics software. Unlike some drag-and-drop tools, SAS offers a powerful programming approach, giving you fine-grained control over data. Its enduring popularity, especially in regulated industries like banking (BFSI) and pharmaceuticals, comes from key strengths:
- Unmatched Data Security & Stability: For large enterprises, the cost of software is minor compared to the risk of data breaches or unstable systems. SAS’s proven reliability and security make it the trusted choice for mission-critical processes.
- Superior Technical Support: SAS provides excellent support and maintains a strong user community, which is invaluable when you’re stuck on a complex problem.
- Handles “Bigger-than-RAM” Data: SAS can process datasets larger than your computer’s available memory by efficiently using hard drive storage, a crucial feature for large-scale analytics.
- High Market Value: With over 40,000 customers worldwide, SAS skills are consistently in high demand, often commanding premium salaries.
Getting Started: Your First Steps with SAS Software
The best part about starting your SAS journey? You can access the full software for free.
| Option | Best For | How to Access | Key Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAS OnDemand for Academics | Most beginners | Cloud-based. No installation. Just sign up for a free account online. | Requires internet. Perfect for learning with any computer. |
| SAS University Edition (now Viya for Learners) | Learning offline | Free downloadable virtual machine. | Runs on your local machine (requires virtualization software). No internet needed after setup. |
The SAS Ecosystem: Key Components and Modules
SAS is a vast suite. As a beginner, you’ll primarily work with Base SAS. Once comfortable, you can explore specialized modules:
- SAS/STAT: For advanced statistical procedures like regression, ANOVA, and predictive modeling.
- SAS/GRAPH: Creates high-quality graphs, charts, and plots for visualization.
- PROC SQL: Allows you to use SQL queries within SAS for powerful data manipulation.
- SAS Macros: A tool for automating repetitive tasks and building dynamic programs.
The Heart of SAS Programming: DATA Step vs. PROC Step
Every SAS program is built on two fundamental building blocks: the DATA step and the PROC (procedure) step. Understanding this distinction is critical.
| Component | Primary Purpose | Analogy | Common Statements |
|---|---|---|---|
| DATA Step | To read, clean, manipulate, and create datasets. It’s where you prepare your data for analysis. | The kitchen prep—washing, chopping, and marinating ingredients before cooking. | DATA, INPUT, SET, INFILE, CARDS |
| PROC Step | To analyze, report on, and visualize data. It’s where you perform the actual analysis on your prepared data. | The cooking and serving—applying heat, combining flavors, and plating the dish. | PROC PRINT, PROC MEANS, PROC SORT, PROC FREQ |
Deep Dive into the DATA Step
The DATA step is your data workshop. Here, you can:
- Import Data: Read data from Excel (
.xlsx), CSV (.csv), text files, or databases. - Create & Transform Variables: Calculate new fields (e.g., Profit = Revenue – Cost).
- Clean Data: Handle missing values (represented by a period
.for numeric data), filter rows, and subset columns. - Combine Datasets: Merge or append multiple datasets together.
Understanding SAS Libraries: Datasets are stored in libraries. The default WORK library is temporary (data is lost when you close SAS). For permanent storage, you use the LIBNAME statement to assign a library to a folder on your computer.
Deep Dive into the PROC Step
Once your data is ready, PROC steps are your analytical engine. With a single statement, you can generate complex reports. For example:
PROC MEANS: Calculates simple statistics like mean, median, min, and max.PROC FREQ: Creates frequency tables and cross-tabulations.PROC PRINT: Displays the data in your output window.PROC SORT: Sorts your dataset by one or more variables.
The SAS Programming Workflow in Practice
A typical SAS programming session follows this natural flow:
- Write Code: In the Editor Window, you write your DATA and PROC steps.
- Submit & Check Log: You run the program. The Log Window is your best friend—it shows notes, warnings, and errors. Always check the log!
- View Results: If the program runs successfully, results appear in the Output Window or as HTML results.
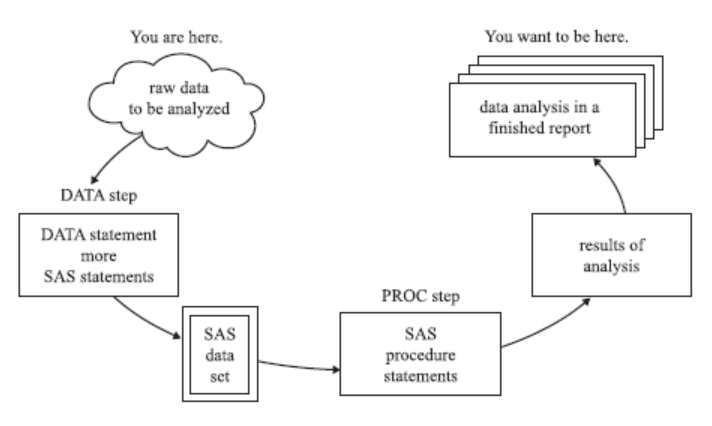
Fig: The SAS Programming Workflow – From raw data to insightful reports.
From Learning to Certification: Validating Your SAS Skills
To boost your career credibility, consider SAS certification. The SAS Institute offers a clear progression path[citation:7]:
| Certification | Target Audience | Exam Format | Core Skills Validated |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAS Certified Specialist: Base Programming | Beginners (3-6 months experience) | Performance-based (write real code)[citation:7] | Accessing data, creating data structures, managing data, generating reports. |
| SAS Certified Professional: Advanced Programming | Experienced Programmers (1+ year experience) | Performance-based[citation:7] | Advanced techniques, SQL, and macro processing[citation:7]. |
Your Learning Roadmap and Next Steps
You can gain working proficiency in Base SAS within 1-2 months of dedicated study. Here’s a practical roadmap:
- Week 1-2: Foundations. Install free SAS, learn the interface, understand libraries, and write simple DATA steps to read and create small datasets.
- Week 3-4: Core Procedures. Master essential PROC steps like
PRINT,SORT,MEANS, andFREQ. - Month 2: Integration & Practice. Work on end-to-end projects: import a CSV file, clean it in a DATA step, analyze it with multiple PROC steps, and export results.
- Beyond: Specialize. Dive into statistics with SAS/STAT, learn PROC SQL for database-style queries, or start automating with Macros.
How to Get Real Practice
Theory isn’t enough. To learn SAS, you must write code. Here’s how to practice:
- Use Built-in Datasets: SAS comes with practice datasets like
SASHELP.CLASS. Use them to experiment. - Find Real-World Data: Import data from your work, public datasets from government sites, or data from hobbies (sports, finance).
- Tackle Kaggle Problems: Try solving beginner-friendly data problems on platforms like Kaggle using SAS.
- Build a Portfolio: Save your best programs and outputs. This portfolio is gold for job interviews.
Conclusion: Your Journey Starts Now
Learning SAS opens doors to careers in high-growth fields like business intelligence, advanced analytics, and data science. Start today by signing up for SAS OnDemand for Academics, write your first DATA step, and embrace the process. Remember, every expert was once a beginner. With consistent practice and the resources outlined in this guide, you’ll be well on your way to adding this valuable feather to your cap and significantly upping your market value.
For further structured learning, explore the comprehensive tutorials on sites like TutorialsPoint and ListenData, or consider the formal Coursera SAS Professional Certificate to guide your study with projects and a direct path to certification.







Thank you so much sir for Plus 500 Strong DA Blog Comment Lists 2023 For BackLinks
thanks for sharing
Thank you for helping people get the information they need. Great stuff as usual.
That is a very interesting and practical tidbit of knowledge. I cannot express how grateful I am that you just provided us with this valuable information. Please keep us updated like this. I am grateful that you shared.
Thanks keep reading and sharing
This was an excellent read. I really liked how the topic was explained in a simple and practical way. Looking forward to reading more articles like this.
Thank you for reading! Keep exploring and sharing — knowledge grows when it’s shared.