How to Check open Ports for Live Streaming |Windows |Linux – Easy Guide
In the enormous computing universe that is so interrelated, being able to check open ports in Linux is a must-have skill for sysadmins, security consultants, and anyone who handles a network. Open ports are like doors to your computer that allow data to flow smoothly. Checking open ports is always of great value, no matter if you want to tighten up your systems’ security, fix network problems, or optimize your server’s performance.
In order to have a seamless streaming scenario for your company’s live events, it is very important that you open ports verification. The streaming guide presented in this article is extensive and provides detailed instructions on how to check for open ports for live streaming on both Windows and Mac operating systems, thus eliminating any chances of buffering or other playback interruptions during in-person events or digital exhibits.
You will learn how to perform open port checks in Linux in this article. After reading it, you will know what open ports are, the different types of ports, and the tools and techniques such as netstat, ss, lsof, Wireshark, and nmap for easily managing and troubleshooting network connections in your Linux VPS system.
This article is a step-by-step guide to checking the open listening ports on a Linux system with five widely used networking tools.
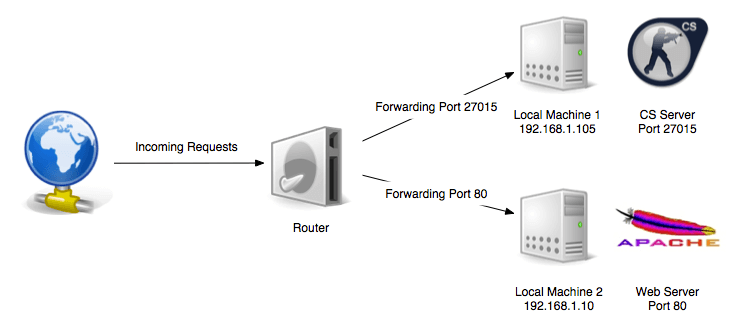
What are Network Ports?
Network ports are typical numerical assignments that allow devices to handle simultaneously the network requests with a single IP address. There are 65535 port numbers in total, and therefore, monitoring which ports are in use can become a bit of a hassle.
How to Check Open Ports on Windows
If you want to find out which ports are open on your Windows system, just follow the steps given in this mini-guide for live streaming:
- Open Command Prompt: Use the shortcut Windows key + R, then type “cmd” and hit Enter to bring up Command Prompt.
- Execute “netstat” Command: Enter “netstat -aon” in Command Prompt and press Enter. With this command, a list of ports and their current statuses will be shown.
- Locate LISTening Ports: The output will reveal port numbers in “LISTENING” state. An open port is a must for streaming in such cases.
- Make a Text File: Port numbers that are not in the “LISTENING” state can be opened manually. For this purpose, enter “netstat -aon > C:\port_test.txt” and hit Enter. The command will generate a .txt file (port_test.txt) containing all open ports.
- Examine the Text Document: Using Notepad or any other text editor, open the file “C:\port_test.txt”. In the document, the port numbers in “LISTENING” state should be allowed by the router for your streaming purpose.
- Adjust Router Settings: Access your router’s settings through a web browser, input the specified port numbers, and apply the changes. This will create the necessary ports for streaming to be opened.
- Retry Streaming: Dismiss the Command Prompt and repeat your streaming activities. The open ports configured freshly should now lead to a better streaming experience.
How to Check Open Ports on Mac
On a Mac, the “netstat” command is one of the ways that can be used to test if ports are opened or closed. Follow the steps below to achieve this:
- Opening the Terminal: Open the Terminal app on your Mac. You can locate it inside the “Utilities” folder that is within the “Applications” folder, or you can search for “Terminal” using Spotlight.
- Type the “netstat” Command: Enter the command below in the Terminal and hit Enter:
netstat -an | grep LISTEN
The result of the command will be a listing of all open ports on your Mac, which are currently in “LISTEN” state. The listing will provide you with port numbers, IP addresses, and the process ID verification service (PID) for those ports.
- Recognizing Applications: In addition to the port numbers and their states, the netstat output will also list respective applications/processes that are utilizing each open port. This info can be quite enlightening in terms of identifying the application linked to a certain open port.
- Checking Port Information: In case you are in doubt about the function of a certain port, you can consult the /etc/services file. This file contains a list of services along with their corresponding port numbers that are known and have already been assigned. To access the content of this file, execute the command below:
cat /etc/services
The file will inform you about some of the services related to the specific port numbers.
By using these commands in Terminal, one can detect the open ports on a Mac and also find out the applications or processes that are making use of these ports. This knowledge can be very handy for troubleshooting and managing the network, especially for the programmers and others who are using a Mac for such purposes.
How to Check Open Ports in Linux?
To check for listening ports on your system using different commands, you can follow these steps:
Using netstat command:
1. Open your terminal.
2. Use the following command to display listening ports:
sudo netstat -tunpl
Here’s what each option does:
– `-t`: Queries for TCP ports.
– `-u`: Queries for UDP ports.
– `-n`: Avoids DNS lookup and displays only IP addresses to speed up the process.
– `-p`: Displays the process ID and the name of the program using the port.
– `-l`: Outputs listening ports.
3. Identify the listening ports/sockets by checking the “State” column and looking for the label “LISTENING.”
Using ss command
1. Open your terminal.
2. Use the following command to scan for listening TCP and UDP ports:
sudo ss -tunl
3. The listening ports/sockets will be marked as “LISTEN” in the “State” column.
Using nmap command
1. Open your terminal.
2. Use the following command to scan for all open TCP and UDP ports on the local system:
sudo nmap -n -PN -sT -sU -p- localhost
Here’s what each option does:
– `-n`: Skips DNS resolution.
– `-PN`: Skips the discovery phase.
– `-sT` and `-sU`: Specify to scan for TCP and UDP ports, respectively.
– `-p-`: Scans all the ports.
These commands will provide you with a list of listening ports on your system, which can be helpful for various network management and troubleshooting tasks.
Trouble Shooting Open Ports Problems
Troubleshooting and addressing common issues during port scanning is crucial for obtaining accurate and effective results. Here are some key considerations for handling firewall restrictions, dealing with false positives and false negatives, and debugging network connectivity problems:
Handling Firewall Restrictions:
- Check Firewall Rules: Ensure that your firewall rules permit traffic to the ports you intend to scan. Adjust these rules if necessary to allow the desired traffic.
- Use Appropriate Scan Techniques: Depending on the firewall’s configuration, consider using scan techniques like SYN scans (e.g., TCP SYN scan with nmap) to evade certain firewall restrictions.
- Scan from Within the Network: Scanning from within the same network as the target system may bypass external firewall restrictions. Try conducting scans from a different system within the network.
- Obtain Proper Authorization: Always ensure you have the necessary authorization to perform port scans, especially on systems you don’t own. Unauthorized scanning can lead to legal and ethical issues.
Dealing with False Positives and False Negatives:
- Verify Results: Cross-check results from multiple scanning tools to validate findings. Consistent reports from different tools make results more reliable.
- Tune Scan Parameters: Adjust scanning parameters, such as timing and technique, to reduce false results. Slower scans with appropriate timing settings can help minimize false positives.
- Check Target System’s State: Confirm that the target system is in the expected state. Misconfigured or unstable systems can lead to false positives.
- Account for Firewall Filtering: Be aware that firewalls and intrusion detection systems can impact scan results. Understand the network environment and the presence of security measures.
Debugging Network Connectivity Problems:
- Check Network Configuration: Verify the correctness of your network configuration, including DNS settings and routing tables.
- Test Connectivity: Use standard network troubleshooting tools like
pingto test connectivity to the target system. Ensure you can reach the target system before attempting port scans. - Inspect Network Hardware: Examine network hardware, such as routers, switches, and cables, for physical issues that might disrupt connectivity.
- Review Firewall Rules: Review firewall rules and access control lists (ACLs) to ensure they are not blocking your scanning traffic.
- Consider Network Load: High network traffic or congestion can affect scan results. Schedule scans during periods of lower network activity.
- Use Appropriate Scan Techniques: Choose scan techniques and parameters that align with the target network’s characteristics. For instance, use more aggressive scans for local networks and stealthier scans for external networks.
Summary
To sum up, determining the open ports on Linux is an essential skill for the system administrators, network professionals, and security experts. There are a number of very robust tools and techniques to make this task easier such as command-line utilities like netstat and ss, the extensive network scanning instrument nmap, and the very detailed information given by lsof. Accurate and effective port scanning is largely dependent on the proper troubleshooting and tackling of the common issues.
F.A.Q
1. What are open ports, and why should I check them?
Open ports are communication endpoints on a computer or network device. Checking open ports is essential for network administrators and security professionals to ensure proper network functioning, identify vulnerabilities, and maintain security.
2. How do I check for open ports on my computer or network?
You can use command-line tools like netstat, ss, and network scanning utilities like nmap to check for open ports. These tools provide insights into active ports on your system or network.
3. What common issues might I encounter when checking open ports?
Common issues include firewall restrictions, false positives (incorrectly identifying open ports), false negatives (missing open ports), and network connectivity problems.
4. How do I handle firewall restrictions when scanning for open ports?
Review and modify firewall rules to allow traffic to the ports you want to scan. Consider using appropriate scan techniques, such as SYN scans, to evade firewall restrictions.
5. What should I do if I encounter false positives or false negatives during port scanning?
Verify results by cross-checking with multiple scanning tools. Adjust scanning parameters and techniques to minimize false results. Ensure that the target system is in the expected state and account for firewall filtering.
6. How can I troubleshoot network connectivity problems during port scanning?
Verify your network configuration, test connectivity using tools like ping, inspect network hardware for physical issues, review firewall rules, and consider the network load. Choose appropriate scan techniques for the target network.
Proper authorization is crucial to avoid legal and ethical issues. Unauthorized port scanning can lead to consequences, so always ensure you have the necessary permissions to perform scans.
8. Are there different methods for checking open ports on Windows and Mac systems?
The methods for checking open ports are generally similar across different operating systems, using tools like netstat or ss. However, the specifics may vary slightly. For Windows, you can use the Windows Firewall settings, while Mac users may rely on the Terminal or System Preferences.
9. What are some best practices for accurate and effective port scanning?
Best practices include using multiple scanning tools, verifying results, adjusting scan parameters, understanding the target system’s state, considering network environment factors, and obtaining proper authorization.