Beginners Guide to SAS Programming
Now, if you are a statistician and need to make sense out of massive data, then having a tool doing that for you can be handy for you. So, if you are a beginner in SAS programming, this guide is intended for you only. Now it is befitting to learn a little of the origin of the programming language you have planned to know.
SAS (formerly “Statistical Analysis System”) is a software for statistical created by SAS Institute for efficiently managing data, analytic tools, multivariate statistical analysis, business intelligence, and predictive analytics. SAS was established at North Carolina State University between 1966 and 1976 until it was founded as SAS Institute. In the 1980s and 1990s, it further enhanced SAS with new statistical processes and extra components.
Now learning a language doesn’t require any pre-requisite, just like you have learned your mother-tongue by listening and following your parents around you. Likewise, it will be beneficial if you have people around capable of computer coding. That would not only give you a great sense of support for times when you find it difficult to move forward, but if you are an absolute beginner and a little introvert, you be the judge if you have managed to learn something up from this blog. That will be our win, so we welcome you again to a journey of a lifetime towards picking up a new feather to your cap and up your value in the market.
As we have confessed, we will start with a correspondent study about java programming. If you have knowledge of prior programming and are comfortable finding solutions by looking for java programming help, you are more than ready to take on SAS.
The computer is just a ‘Monkey’; you only tell it what to do, and it does. The process is generally called programming. It is not inconsistent in the case of SAS programming. SAS generally demands working with massive data, and the below diagram speaks for its own.
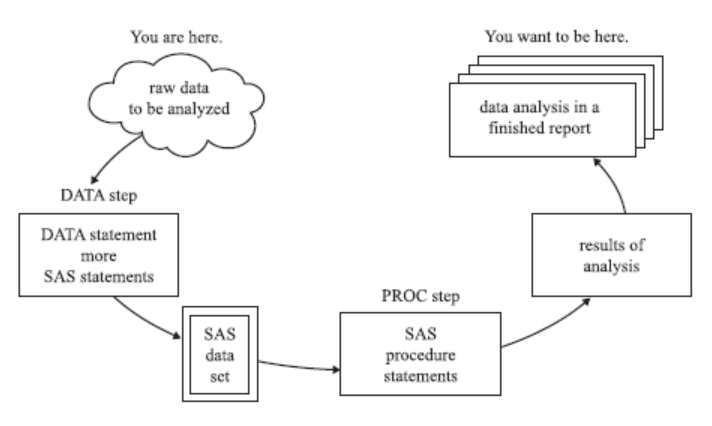 Fig: Showing what you are expected with your newly acquired knowledge in SAS. (Source: owardsdatascience.com)
Fig: Showing what you are expected with your newly acquired knowledge in SAS. (Source: owardsdatascience.com)
Let us break the process for you,
-
DATA Step-
The data phase contains all SAS statements starting with line data and finishing with line data lines. It allows you to describe and edit your data. In the DATA phase, four expressions we use typically.
- The DATA statement identifies the dataset.
- The variable names we list in the INPUT statement.
- The CARDS statement suggests that data lines will follow quickly.
- The INFILE statement indicates that data is stored in a file and provides the file’s name.
-
PROC Step-
AS you have rightly guessed, PROC stands for Procedures. By writing a query (method of getting your desired result), you are sure to get your desired outcome. But imagine doing the same every single time. That is why we write procedures to do the hard work once and rip the benefit. The average/mean can calculate using SAS’s basic procedure.
The PROC steps inform SAS about the data analysis, such as modeling, variance analysis, Mean, Median, and mode computation, and so on. The PROC keyword appears at the beginning of every PROC statement.

-
SAS Programming basics-
The main steps revolve around getting the desired data as expected, efficiently writing procedures to work with your data as per your requisition, and visualizing your dataset and results.
-
We are importing SAS data.
Data in the SAS environment can be of two types, permanent and temporary. By default, SAS takes data temporarily; you as a developer need to decide the life snap of your data. Storing data to files and starting working from there can ensure data becomes permanent.
-
Perform descriptive statistical analysis.
Most of the time, the data you get for analysis can be massive, and that too runs the risk of missing critical values throughout. The first step is to find these missing values. SAS by default represents missing value function by a period(.). You now need to write procedures to work with your data. These steps are essential for interpreting the data to your benefit and serve the purpose of your analysis.
-
I am plotting graphs for visualization.
Statistics are made widely accepted and read by using graphs and charts to show the intended message. Be that it as an analysis of a small dataset to larger datasets. There can be multiple visualization tools at your disposal. From Histogram to scatter plot and simple Bar chart to Box plot, SAS has an array of options for you to choose from.
We believe we have made justice to your time spent to get an overall idea about SAS programming and starting around. Be sure to check our budget-friendly services for your various programming help. We advise you to go through the added materials and use them to your benefit. We would be more than happy if you find the same helpful.
SAS Certification Prep Guide: Base Programming for SAS – can be your go-to guide if you want to show off your knowledge by acquiring a Certification.




Thank you so much sir for Plus 500 Strong DA Blog Comment Lists 2023 For BackLinks
thanks for sharing
Thank you for helping people get the information they need. Great stuff as usual.