How to Generate a Google Translate API Key: A Comprehensive Guide
If you’ve ever wanted to integrate the powerful translation capabilities of Google Translate into your applications, websites, or services, you’ll need a Google Translate API key. This key allows you to access the Google Translate API and utilize its features to provide seamless translation experiences to your users.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the process of generating a Google Translate API key step by step. We’ll cover everything from creating a project in the Google Cloud Platform, enabling the Translate API, setting up billing, and obtaining your API key. So let’s dive in and learn how to generate a Google Translate API key!
Understanding the Power of Cloud Translation API
Before diving into the technical setup, it is crucial to understand the infrastructure you are accessing. The Google Cloud Translation API is not merely a dictionary tool; it utilizes Neural Machine Translation (NMT) technology. Unlike legacy phrase-based machine translation (PBMT), NMT translates entire sentences at a time, using deep learning models to predict the most relevant output based on broader context.
For developers and webmasters managing multi-lingual sites—such as those on WordPress using plugins like WPML or custom PHP scripts—accessing the V3 or V2 API endpoints provides enterprise-grade scalability. Whether you are automating the localization of a University portal or building a dynamic Chrome extension, the API key is your authentication token that links your request to Google’s massive linguistic datasets.
Cloud Translation Basic vs. Advanced
When you enable the API, you are generally tapping into one of two tiers provided by Google Cloud Platform (GCP):
- Cloud Translation – Basic (v2): Ideal for simple text translation, language detection, and most standard web development use cases. This is what most WordPress translation plugins require.
- Cloud Translation – Advanced (v3): Offers features like glossary support (to enforce specific brand terminology), batch translation for large files, and AutoML custom model integration.
How to Generate a Google Translate API Key
To generate a Google Translate API key, follow the steps outlined below:
Step 1: Create a Project in Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
The core of any Google Cloud activity is the “Project.” A project organizes all your Google Cloud resources. It consists of a set of users, a set of APIs, billing settings, and permissions.
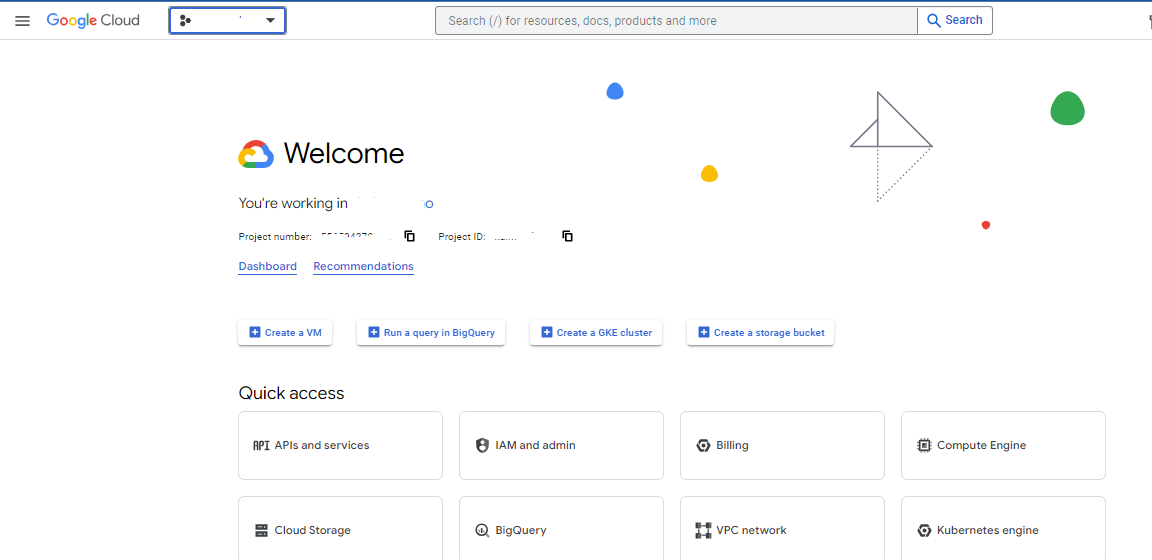
- Visit the Google Cloud Platform website and sign in with your Google account. Ensure you are using the Google account associated with your organization or the specific development environment you intend to manage.
- Create a new project by clicking on the project drop-down menu at the top of the screen (often labeled “Select a project”) and selecting “New Project.”
- Enter a descriptive name for your project (e.g.,
My-Translation-App-2026) and click “Create” to initialize the project in GCP. The system will assign a unique Project ID, which you may need later for server-side authentication.
Step 2: Enable the Google Translate API
By default, new projects have no APIs enabled to save resources and improve security. You must explicitly authorize the “Cloud Translation API.”
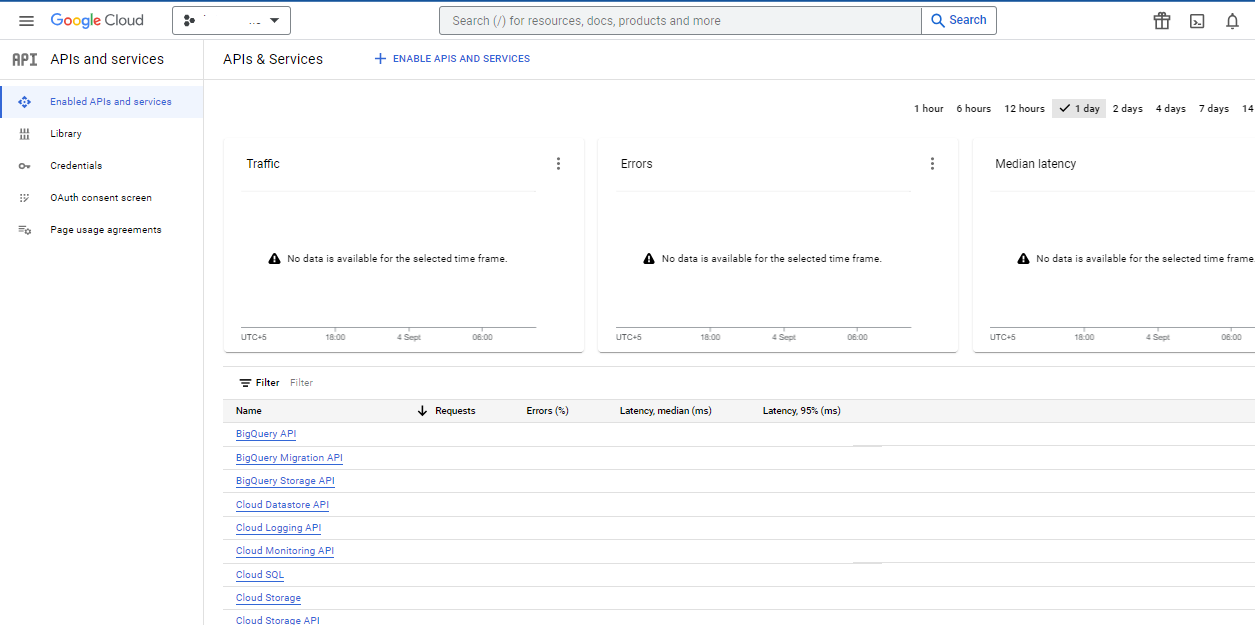
- In the GCP Console, navigate to the APIs & Services section via the hamburger menu in the top-left corner.
- Click on “Library” in the left sidebar to access the massive Google API Library.
- In the search bar, type “Cloud Translation API” (or simply “Google Translate”) and click on the result titled Cloud Translation API.
- Click the blue “Enable” button. This process may take a few moments as Google provisions the necessary resources for your project.
Step 3: Set Up Billing
Google requires a billing account for all Cloud projects, even if you stay within the free tier. This is to verify identity and cover potential overages.
- Navigate to the Billing section in the GCP Console.
- Select your project from the project drop-down menu if it isn’t already selected.
- Click on “Link a billing account.” If you have an existing billing account, select it. If not, click “Create Billing Account” and follow the instructions to enter your credit card or bank details. A valid billing account is required to use the Google Translate API.
Pro Tip: Set up “Budget Alerts” immediately after enabling billing. This ensures you receive an email if your API usage accidentally spikes, preventing unexpected costs.
Step 4: Create Credentials and Obtain API Key
Now that the service is enabled and billing is attached, you need the “key” to open the door.
- Go back to the APIs & Services section in the GCP Console.
- Click on “Credentials” in the left sidebar. This dashboard manages API Keys, OAuth 2.0 Client IDs, and Service Accounts.
- Click on the “+ Create Credentials” button at the top and select “API key” from the dropdown list.
- Your API key will be generated immediately in a pop-up window. Click the “Copy” icon to copy it to your clipboard.
Congratulations! You have successfully generated a Google Translate API key. Keep this key secure, as it grants access to the Google Translate API and should be treated like a password.
Securing Your API Key: Mandatory Best Practices
In the world of DevOps and API management, an unrestricted API key is a significant security vulnerability. If a malicious actor obtains your key, they can exhaust your quota or run up your billing. Google Cloud Platform uses an Identity and Access Management (IAM) framework, but for simple API keys, you must apply “Application Restrictions.”
How to Apply HTTP Referrer Restrictions
If you are using this API key on a WordPress website (client-side or server-side), you should lock the key so it only accepts requests from your specific domain.
- Return to the Credentials tab where you created the key.
- Click on the name of the API key (usually “API key 1”) to edit its settings.
- Under “Application restrictions,” select HTTP referrers (web sites).
- Add your website URLs in the following formats to cover all subdomains and protocols:
*example.com/**example.com
- Under “API restrictions,” select Restrict key and check Cloud Translation API. This ensures that even if the key is stolen, it cannot be used for other expensive services like Google Maps or Compute Engine.
Validating Your API Key with Code
Before integrating the key into a complex plugin or application, it is wise to test it using a simple cURL command or a PHP script. This confirms that the key is active, billing is correctly linked, and the Cloud Translation API is responding.
Testing via URL (REST)
You can test the key directly in your browser or a tool like Postman by navigating to the following URL (replace YOUR_API_KEY with the key you just generated):
https://translation.googleapis.com/language/translate/v2?key=YOUR_API_KEY&source=en&target=es&q=Hello%20World
If successful, you will receive a JSON response containing the translated text (“Hola Mundo”).
Simple PHP Implementation Example
For developers creating custom functionality, here is a basic PHP function to utilize your new key. This utilizes cURL to communicate with the Google server.
<?php
function gsg_translate_text($text, $target_lang) {
$apiKey = 'YOUR_GOOGLE_API_KEY';
$url = 'https://translation.googleapis.com/language/translate/v2?key=' . $apiKey . '&q=' . rawurlencode($text) . '&source=en&target=' . $target_lang;
$handle = curl_init($url);
curl_setopt($handle, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, true);
$response = curl_exec($handle);
curl_close($handle);
$decoded = json_decode($response, true);
if (isset($decoded['data']['translations'][0]['translatedText'])) {
return $decoded['data']['translations'][0]['translatedText'];
} else {
return "Error: " . $response;
}
}
?>
Google Translate API vs. DeepL API: Which is Right for You?
While Google Translate is the industry giant for raw volume and language breadth, DeepL has emerged as a significant competitor, particularly noted for its high-quality European and Asian language translations. Choosing between the two often comes down to a trade-off between “Global Reach” (Google) and “Linguistic Nuance” (DeepL).
| Feature | Google Cloud Translation API | DeepL API |
|---|---|---|
| Language Support | 130+ languages (Including low-resource dialects) | ~30+ languages (Major European & Asian) |
| Pricing Model | First 500k chars/month free. Then ~$20 per million chars. | First 500k chars/month free (Free Tier). Then ~$25 per million chars (Pro Tier). |
| Translation Quality | High accuracy, but can be literal. Excellent for cross-referencing diverse languages. | Superior nuance and fluency. Often indistinguishable from human translation in supported pairs. |
| Data Security | Enterprise-grade (ISO/IEC 27001). No data logging if configured correctly. | Pro API guarantees data deletion. Free API may use data for training. |
| Document Translation | Supported (PDF, DOCX, PPTX, XLSX) preserving formatting. | Excellent formatting preservation, arguably superior for PDF handling. |
Critical Analysis: When to Switch?
If you are building a website targeting a global audience—for example, a news portal that needs to be accessible in Vietnamese, Swahili, and Urdu—Google Translate API is your only viable option due to its massive language database.
However, if your business focuses strictly on the EU or US markets (English, German, French, Spanish, Italian), developers often report that DeepL provides a more natural reading experience. DeepL’s API is slightly more expensive per character once you exceed the free tier, but the reduction in post-editing work (the human effort needed to fix AI mistakes) can offset the cost difference.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Here are some common questions related to generating a Google Translate API key:
Q: Is the Google Translate API free?
A: No, the Google Translate API is not free. While Google does offer a free tier for the API (currently the first 500,000 characters per month are free), it has usage limits, and beyond that, you will be charged according to the pricing structure provided by Google Cloud Platform.
Q: Can I use the same API key for multiple projects?
A: Yes, you can reuse the same Google Translate API key across multiple projects within your Google Cloud Platform account. It’s a convenient way to manage your API keys and keep track of usage.
A: To add restrictions to your API key, you can configure API key restrictions in the APIs & Services section of the GCP Console. You can restrict the key to specific APIs, IP addresses, or HTTP referrers.
Q: What is the difference between Service Accounts and API Keys?
A: API Keys are simple encrypted strings used to identify a project for quota and billing purposes, ideal for client-side or simple server-side requests. Service Accounts are special Google accounts that belong to your application or a virtual machine (VM), not an individual end-user, and are recommended for server-to-server interactions where higher security is required.
Q: How do I troubleshoot a “403 Permission Denied” error?
A: A 403 error typically means one of three things: either the “Cloud Translation API” was not enabled in the Library (Step 2), the billing account linked to the project is inactive or has payment issues (Step 3), or your API Key restrictions (HTTP referrers) do not match the website sending the request.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive guide, we explored the process of generating a Google Translate API key. We covered the necessary steps, from creating a project in the Google Cloud Platform to enabling the Google Translate API, setting up billing, and obtaining your API key. Remember to keep your API key secure and follow best practices for its usage.
Now that you have your Google Translate API key, you can unlock the power of Google Translate and enhance your applications, websites, or services with seamless translation capabilities. So go ahead and start leveraging the Google Translate API to break down language barriers and connect with users around the world!






