Unlocking Success with Google Search Operators for SEO (2026 Advanced Edition)
The Power of Google Search Operators for SEO in the AI Era
In the vast landscape of the internet, where billions of websites compete for attention and AI-generated overviews now dominate the first fold of search results, the role of search engine optimization (SEO) cannot be underestimated. Among the many tools at an SEO expert’s disposal, Google Search Operators stand out as a potent arsenal for fine-tuning searches and extracting valuable insights. Whether you’re a seasoned SEO professional or just starting your journey, understanding and harnessing these operators can significantly impact your website’s performance.
⏱️ 2026 Reality Check: Why This Still Matters
While many SEOs rely solely on third-party crawlers, those tools often lag by weeks. Search operators query Google’s live index in real-time, revealing competitor moves, indexation bloat, and security leaks before they appear in any dashboard [citation:4][citation:5]. This is your “source of truth” layer.
What are Google Search Operators?
Google Search Operators are specialized queries or symbols used to refine search queries, providing more precise and targeted search results. These commands are essential for fine-tuning your searches and uncovering results tailored to your specific needs. For example, if you want to find search results exclusively from the website Meetanshi.com, you can use the “site:” operator. This operator limits the search to that particular website, making your search results highly focused.
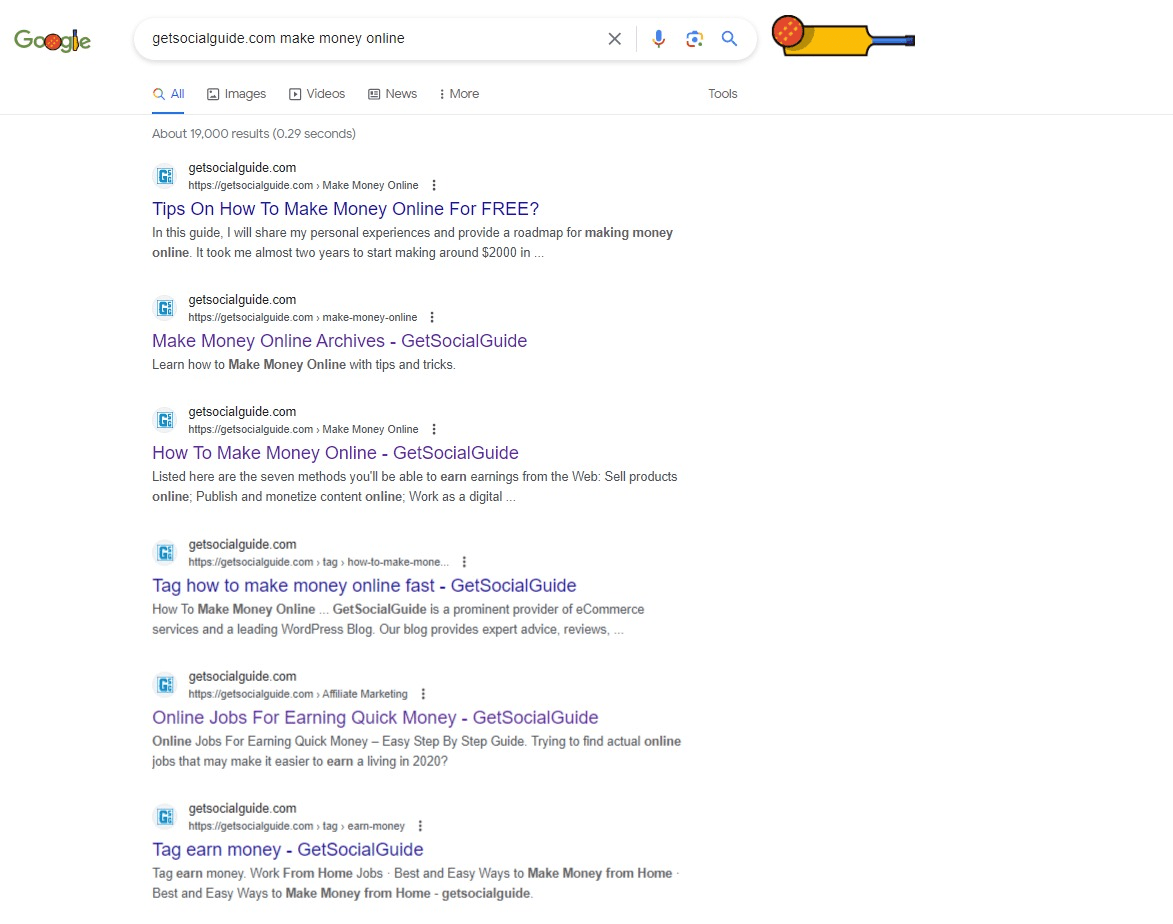
These specialized Google Search Operators include distinct queries and symbols designed to help you achieve more accurate search outcomes. They play a vital role in refining your searches, enabling you to discover highly specific results. For instance, if your goal is to retrieve search results only from Meetanshi.com, you can utilize the “site:” operator.
⚠️ Deprecation & Unreliability Alert
While Google Search Operators offer valuable shortcuts for refining searches, it’s important to note that some of them have limitations and may not always work as expected. Google has officially deprecated inanchor:, link:, and info: [citation:3][citation:5]. The AROUND(#) operator is sporadic. Here are some examples of potentially unreliable Google Search Operators:
- #..# Operator: This operator displays results within specified numeric ranges. For example, “old laptops $200..$300” would search for products in that price range. (Works intermittently)
- inanchor: Operator: It searches for pages with the specified term in the anchor text of links. (Mostly deprecated)
- allinanchor: Operator: This operator searches for pages with all the specified terms in the anchor texts of links. (Deprecated)
- AROUND(#) Operator: It searches for pages where both terms appear within a close distance of the specified number of words. (Unreliable in 2026)
These operators can be helpful, but it’s important to be aware of their limitations and understand that they may not consistently deliver the desired results. Always verify using the cache: operator or live crawls.
Google Search Operators for SEO: Unveiling Their Potential
Google Search Operators, essentially advanced commands, are used to refine search queries and retrieve highly specific results. They allow you to delve deeper into Google’s index and extract information that might not be easily accessible through regular searches. These operators are a treasure trove for SEO practitioners, enabling them to analyze competitors, find link-building opportunities, and discover niche-specific content.
Competitor Intelligence & Real-Time Spying (2026 Tactics)
In the current landscape, real-time competitive intelligence separates proactive SEOs from reactive ones. Using search operators, you can replicate the functionality of expensive tools with higher freshness [citation:1][citation:4].
Content Velocity & Silent Pivots
By running site:competitor.com and filtering by “Past month” (or using after:2026-01-01), you can instantly see content velocity. If a competitor suddenly publishes 50 new pages on “AI workflow,” you’ve identified a strategic pivot before the press release [citation:4].
Use the wildcard operator: site:*.competitor.com. This reveals subdomains like dev.competitor.com, staging.competitor.com, or meetup.competitor.com. These areas often leak upcoming product features or beta tests [citation:1][citation:5].
🔥 Pro Tip: The “Filetype” Leak Hack
Search site:competitor.com filetype:pdf "pricing" OR "roadmap". Companies often index investor decks and sales one-pagers that aren’t linked anywhere else. This is your highest ROI for competitive research [citation:4][citation:5].
List of Google Search Operators (100% Working – Verified 2026)
Below is a revised version of the list of Google Search Operators you provided:
Here’s an extensive list of Google Search Operators that you can utilize to enhance your search refinement. These operators have been thoroughly tested in Q1 2026 and are guaranteed to function effectively.
| Operator | Definition | SEO Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| “” | Exact match phrase | Find duplicate content / brand mentions |
| OR / | | Boolean OR | Track brand variations (e.g., “GSG” OR “Google Search Guide”) |
| AND | Boolean AND | Narrow results (default) |
| – | Exclusion | Remove noise (-site:pinterest.com -jobs) |
| * | Wildcard | Fill in missing words (“best * for SEO”) |
| () | Grouping | Complex boolean logic |
| define: | Dictionary | Quick definitions for snippet optimization |
| cache: | Cached snapshot | Check last crawl date |
| filetype: / ext: | File format filter | Find PDF guides, PPT templates, XLS backlink lists |
| site: | Domain restrict | Indexation audit, competitor size |
| related: | Similar sites | Competitor discovery, link prospecting |
| intitle: | Title tag search | Content gap analysis |
| allintitle: | All words in title | Check exact headline competition |
| inurl: | URL search | Find categories (/blog, /resources) |
| allinurl: | All words in URL | Deep structure analysis |
| intext: | Body text search | Entity adoption tracking |
| allintext: | All words in body | Comprehensive topic presence |
| weather: | Local weather | Local SEO context |
| stocks: | Stock data | Financial SERP features |
| after: | Date filter (post) | Fresh content discovery |
| before: | Date filter (pre) | Historical analysis |
| loc: | Location filter | Hyperlocal SERP simulation [citation:6] |
| source: | News source filter | PR monitoring |
“” (Exact Match)
Search for precise-match phrases or words. For instance, using “Apple” will yield results containing the exact word “Apple.”
OR
Search for results matching either of two terms. Occasionally, results may encompass both terms. For example, “Apple OR Google” will present results containing either Apple or Google.
|
An alternative to the OR operator. For instance, “Apple | Google.”
AND
Search for results that match both terms. For instance, “Apple AND Google” will display results relevant to both Apple and Google. (Google defaults to AND, but explicit usage helps with complex strings).
– (Minus / Exclude)
Exclude pages that lack specific terms or meet certain conditions. For example, “Apple -iPhone” will exhibit pages related to Apple but not mentioning iPhone. Crucial for cleaning SERPs.
* (Wildcard)
Wildcard character for Google search. It fills in missing words or phrases. For instance, “best * in San Diego” will retrieve results containing any phrase in place of the wildcard.
()
Group multiple search terms or operators for desired outcomes. For instance, “Apple (iPhone OR iPad)” will display results pertinent to either Apple iPhone or Apple iPad.
define:
Retrieve definitions of terms from Google’s dictionary, knowledge panel, or relevant results. For example, “define:search engine optimization” will offer the definition of SEO along with relevant information.
cache:
Access the cached version of a webpage from Google. For example, “cache:https://meetanshi.com” will provide the latest checked copy of the Meetanshi homepage.
filetype:
Search for specific file types (pdf, doc, etc.). For instance, “Google Search Operators filetype:pdf” will return PDF results related to Google search operators.
ext:
An alternative to the filetype operator. For example, “Google Search Operators ext:pdf.”
site:
Retrieve results exclusively from a specific website. For example, “site:meetanshi.com SEO” will show SEO-related results only from Meetanshi.
Find websites resembling a particular domain. Note that this may not work for all domains. For example, “related:google.com” will display other sites similar to Google.
intitle:
Locate results with a specific term in the title tag. For example, “intitle:checklist seo” will present results related to SEO containing the word “checklist” in the title tag.
allintitle:
Find results with a specific phrase in the title tag. For example, “allintitle:seo checklist” will show results containing both SEO and Checklist words in the title tag.
inurl:
Locate results containing a specific term in the web address. For example, “inurl:seo-checklist” will return results containing “seo-checklist” in the address.
allinurl:
Find results containing all provided terms in the web address. For example, “allinurl:wordpress seo checklist” will display results containing the words “wordpress,” “seo,” and “checklist” in the address.
intext:
Retrieve results containing specific terms anywhere in the content. For instance, “intext:backlinks” will yield results containing the word “backlinks” anywhere in the content.
allintext:
Find results containing all provided terms anywhere in the content. For example, “allintext:seo checklist” will present results containing both SEO and checklist, regardless of their location within the content.
weather:
Retrieve weather information for any location by name or pin code. For instance, “weather:San Diego.”
stocks:
Search for stock information by ticker symbol or stock name. For example, “stocks:tesla” will display Tesla stock information from Google Finance.
after:
Display results published or refreshed after a specific date. Use the format yyyy-mm-dd. For example, “after:2023-07-01 seo checklist” will return results related to the SEO checklist published or refreshed after July 1, 2023.
before:
Display results published or refreshed before a specific date. Use the format yyyy-mm-dd. For example, “before:2023-07-01 seo checklist” will show results related to the SEO checklist published or refreshed before July 1, 2023.
in
Convert currencies, measurement units, time zones, etc. For example, “1000 USD in Euro” will provide real-time currency conversion from USD to Euro.
Using Google Search Operators for SEO
To leverage the true potential of Google Search Operators for SEO, you need to understand the syntax and their various applications. By incorporating these operators into your search queries, you can uncover insights that go beyond the surface-level results. Here are some powerful Google Search Operators for SEO:
1. Site Operator – “site:”
Using “site:” followed by a domain allows you to search for content within a specific website. This is invaluable for competitive analysis and identifying indexed pages on your site.
2. Intitle Operator – “intitle:”
With “intitle:”, you can find pages containing your specified keyword(s) in their title. This is ideal for pinpointing your target keywords’ prominence across various websites.
3. Inurl Operator – “inurl:”
The “inurl:” operator helps you discover URLs that contain your designated keyword(s). This is useful for identifying potential backlink opportunities and understanding URL structures.
When you use “related:” followed by a website URL, Google will display websites that are similar in content. This aids in finding websites to collaborate with or to analyze your competitors.
5. OR Operator – “OR”
The “OR” operator allows you to search for either one keyword or another. This is handy for identifying different variations or synonyms of a keyword.
Expanding Your SEO Arsenal: Lesser-Known Google Search Operators
Certainly, here are concise descriptions for some additional Google search operators that advanced SEO auditors use weekly:
-
Cache Operator – “cache:”
Retrieve the cached version of a webpage using the “cache:” operator. This is useful for viewing how a page appeared to Google’s crawler.
-
Filetype Operator – “filetype:”
Use “filetype:” followed by a specific file extension to locate documents of a particular type. Valuable for research and analysis.
-
Info Operator – “info:”
The “info:” operator offers details about a webpage. (Note: Partially deprecated in 2026; use third-party tools for backlink data) [citation:3].
-
Define Operator – “define:”
For quick definitions, use the “define:” operator to access concise explanations from various sources.
-
loc: Operator
Filters results to a specific location. Example:
sushi loc:94043[citation:6]. -
source: Operator
Limits Google News results to a specific publication. Example:
source:TechCrunch[citation:6].
Feel free to ask if you have more questions or need further assistance!
Optimizing Your SEO Strategy with Google Search Operators
Embracing Google Search Operators as an SEO professional can lead to profound outcomes for your strategy. These operators provide you with the ability to:
- Perform Comprehensive Competitive Analysis: Assess competitors’ backlinks, content strategies, and keyword optimization to gain insights into their approach.
- Detect Broken or Outdated Links: Identify broken links on your website to enhance user experience and bolster your SEO efforts.
- Uncover Guest Posting Opportunities: Locate websites accepting guest contributions within your niche, enabling you to broaden your reach.
- Generate Fresh Content Ideas: Analyze popular topics and related search queries to discover new avenues for creating engaging content.
- Monitor Indexed Pages: Keep track of your website’s indexed pages to ensure all pertinent content is easily discoverable.
These operators empower you to refine your SEO approach and achieve remarkable results. If you have further inquiries or need assistance, please don’t hesitate to ask!
Different Ways to Use Google Search Operators for SEO
Find Indexing Issues: Utilize the site: operator to discover all indexed pages within a domain. This helps assess the size of a website and identify unnecessary indexed pages. You can also apply this to specific web pages to check their indexing status. Utilize the Tools option to find recently indexed pages within a chosen timeframe, or manually use the before: and after: operators to specify a time range. You can even use site:yourwebsite.com intitle:prev_year to locate outdated pages that may require updating.
Find & Analyze Competitors: The related: command can assist in discovering competing domains. Combine various search operators to analyze specific competitors or find content related to a particular topic. For deeper analysis, combine site:competitor.com inurl:blog after:2026-01-01 to see their recent focus areas [citation:4].
Find Guest Post Opportunities: Utilize Google search commands to identify websites that accept guest posts in your niche. Combine keywords with terms like “write for us” to find guest posting sites. Experiment with other terms like “become a contributor,” “contribute guest posts,” and more to expand your search for guest post opportunities.
Find Duplicate Content Issues: Use double quotation marks "" to locate exact matches of phrases or sentences on Google. This helps identify both cross-site and onsite content duplication. Exclude your own domain using -site: to specifically search for duplicate content on other sites. This method can also uncover instances of content theft.
Find Unlinked Brand Mentions: Locate instances where your brand is mentioned without being linked. Use "" and -site: operators to exclude your site and find brand mentions on other sites. Reach out to these sources and request proper attribution with links. This strategy is effective for personal branding as well. Pro tip: Filter by site:.edu or site:.gov for high-authority unlinked mentions [citation:2].
Find Listicles in Your Niche: To have your site featured in listicles, use search operators such as intitle:"best marketing companies" to find relevant listicle articles. Outreach to these websites to have your business included in such articles and gain visibility.
Find Non-Secure Pages: Identify non-secure HTTP pages indexed by using the site:yourwebsite.com -inurl:https search operator. This is important for addressing unsecure content and ensuring a better user experience, as HTTPS is a Google ranking factor.
Find Opportunities for Internal Links: Employ search operators like double quotation marks and site: to locate exact-match results within your own site. Use the intitle operator to find pages with specific titles. These operators aid in identifying opportunities for creating effective internal links.
In addition to these methods, there are various other ways to leverage Google search operators for SEO. Experiment with different combinations to enhance your search refinement and achieve better SEO outcomes.
Find Guest Post Opportunities
Google search commands offer a valuable tool for discovering websites that welcome guest posts in your specific niche. You can enhance your search by combining relevant keywords with terms like “write for us” to identify guest posting opportunities.

Moreover, there are various other terms you can try to locate websites that accept guest contributions. Here are some of those terms:
- [topic] “become a contributor”
- [topic] “become a guest writer”
- [topic] “contribute guest posts”
- [topic] “guest article”
- [topic] “guest author”
- [topic] “guest post written by”
- [topic] “our editorial guidelines”
- [topic] “our guest post guidelines”
- [topic] “submit an article”
- [topic] “we are accepting guest articles”
- [topic] “write an article for us”
- [topic] “write for us”
You can also experiment with using the intitle or inurl operators to narrow down your search and find specific guest post pages. Similarly, you can employ these techniques to identify websites that accept sponsored posts as well.
Find Unlinked Brand Mentions
Numerous individuals discuss your brand online without actually including a link to your website. Initiating contact with them and politely requesting a link can be an effective strategy for acquiring valuable backlinks. To identify instances where your brand is mentioned but not linked, you can employ Google search operators, specifically the double quotation marks "" and the -site: operator. For instance, if your brand name is “YourBrandName,” you can use the search command "YourBrandName" -site:yourbrandname.com. This search query will retrieve all the web pages on external sites that mention your brand but exclude any mentions on your own website. To further refine your search, you can utilize the “Tools” option located on the left side of the search results, allowing you to filter these mentions by time. This approach can also be applied when monitoring personal branding mentions for individuals.
⚠️ The CAPTCHA Bottleneck
Manual use of search operators is powerful, but excessive querying (more than 20-30 advanced searches in a short window) will trigger Google to block your IP with CAPTCHAs. For large-scale audits, consider using dedicated SEO platforms that integrate operator logic via APIs [citation:5].
Find Listicles in Your Niche
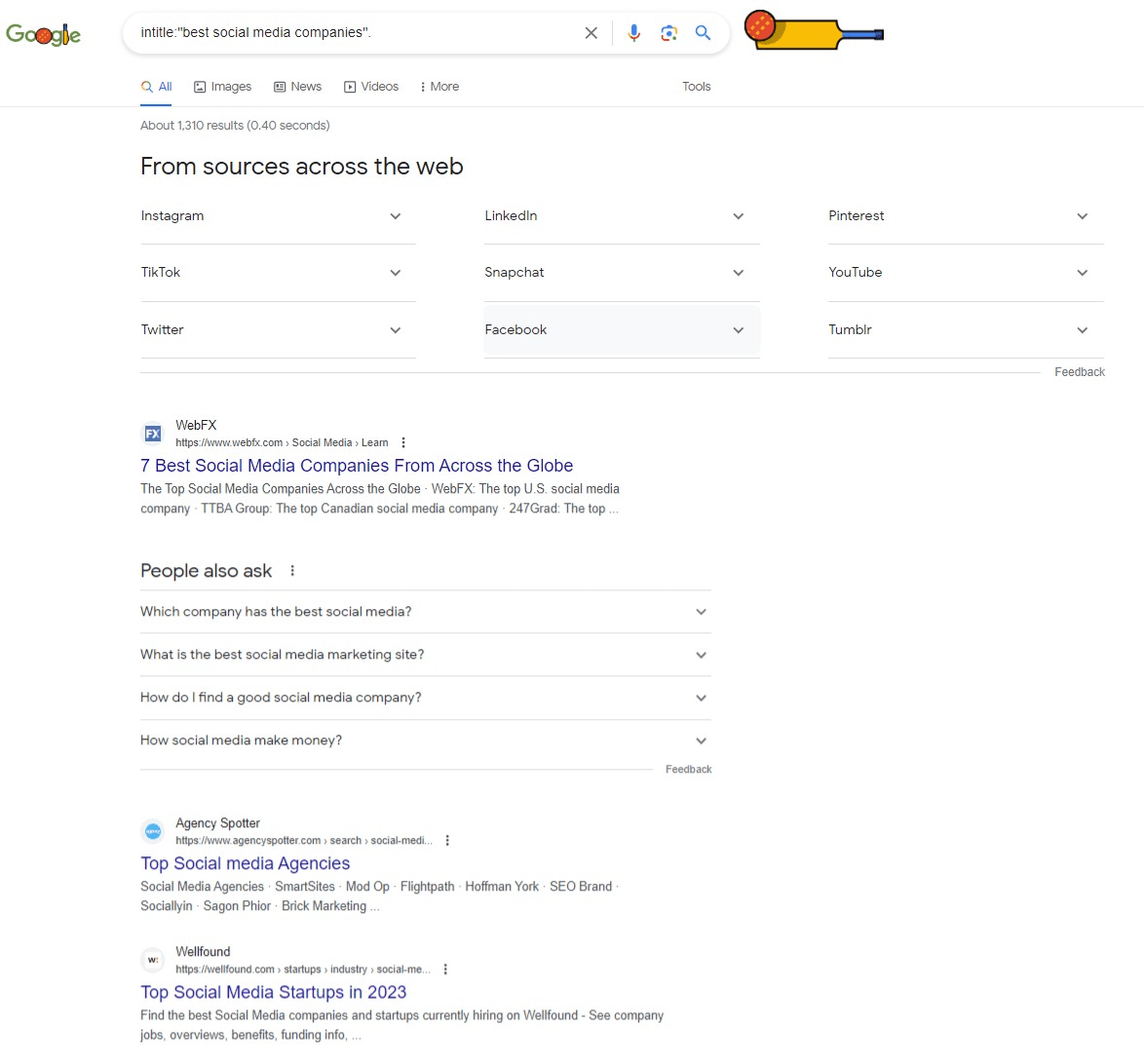
Suppose you’re operating a marketing company and you aspire to have your website featured in listicles, like those ranking the best marketing companies. In this scenario, you can make use of Google search commands to identify such listicles and reach out to them for potential inclusion. For instance, if you’re looking to find listicles titled “best social media companies,” you can employ the search command intitle:"best social media companies". This command will yield a list of relevant listicles with the specified title, providing you with potential opportunities to engage with them.
Advanced Brand Monitoring & Sentiment Analysis Using Operators
In 2026, brand monitoring extends beyond simple backlinks. You must track how AI overviews and forums perceive your brand. Search operators allow you to simulate this [citation:2].
- Reddit Sentiment:
site:reddit.com "YourBrand" (scam OR terrible OR "bad experience") -"thank you"– This surfaces raw, unfiltered user sentiment. - Quora Questions:
site:quora.com "YourBrand"– Find unanswered questions about your product to create FAQ content. - Negative PR Alerts:
"YourBrand" (lawsuit OR recall OR investigation) -site:yourbrand.com.
FAQs about Google Search Operators for SEO
Q: How do I use Google Search Operators effectively?
A: To use Google Search Operators effectively, begin by grasping the syntax of different operators. Experiment with diverse combinations to uncover the specific insights you require. Always ensure no space after the colon (e.g., site:domain.com NOT site: domain.com) [citation:3][citation:5].
Q: Can Google Search Operators replace traditional keyword research tools?
A: While they offer distinctive insights, their optimal utilization involves complementing them with keyword research tools for a comprehensive strategy. Operators are for precision; tools are for scale.
Q: Are there any risks associated with using Google Search Operators?
A: Yes, excessive usage may trigger CAPTCHA challenges from Google. Practice prudence and responsibility in their use. Also, relying on deprecated operators gives false data.
Q: Can Google Search Operators assist in content ideation?
A: Certainly, operators like “intitle:” and “related:” can stimulate ideas for fresh content topics. Use intitle:"ultimate guide" intitle:keyword to see existing guide formats.
Q: Are Google Search Operators limited to web searches?
A: No, they can also be applied to image and news searches, broadening their versatility. Use source: for news and imagesize: for images.
Q: How frequently should I employ Google Search Operators?
A: Utilize them as needed, yet refrain from excessive use to avoid potential limitations on access. A daily “morning 10” routine is highly effective.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of SEO with Google Search Operators
In the ever-evolving realm of SEO, maintaining a competitive edge demands innovative strategies and tools. Google Search Operators present a distinctive lens through which you can navigate the vast expanse of online data, enabling you to extract invaluable insights that can steer your website toward triumph. By integrating these operators into your SEO toolkit and delving into their intricacies, you can unearth hidden potentials, surpass rivals, and establish an enduring imprint in the digital domain.
Remember, mastering Google Search Operators for SEO is both an art and a science. Embrace the journey of learning, adapt to emerging trends, and witness your website ascend to newfound heights in the hierarchy of search engine rankings.