How to make use of the BCG Matrix? – Full Guide
To apply the BCG Matrix you possibly can consider it as exhibiting a portfolio of products or providers, so it tends to be extra related to bigger companies with a number of providers and markets. However, entrepreneurs in smaller companies can use related portfolio considering to their products or providers to spice up leads and gross sales as we’ll present on the finish of this text. Considering every of those quadrants, listed below are some suggestions on actions for every:
What is the BCG Matrix?
Developed by the Boston Consulting Group in 1968, the BCG Matrix remains one of the most enduring strategic planning tools used by businesses worldwide. At its peak, approximately half of all Fortune 500 companies utilized this framework to make critical decisions about resource allocation and portfolio management. Today, it remains a cornerstone of business strategy education.
- Dog products: The standard advertising and marketing recommendation right here is to goal to take away any canines out of your product portfolio as they’re a drain on resources. However, this may be an over-simplification because it’s possible to generate ongoing income with little value. For instance, within the automotive sector, when a car line ends, there’s nonetheless a necessity for spare elements. As SAAB ceased buying and selling and producing new automobiles, an entire enterprise emerged offering SAAB elements.
- Question mark products: As the identify suggests, it’s not identified if they may turn into a star or drop into the canine quadrant. These products usually require important funding to push them into the star quadrant. The problem is that numerous funding could also be required to get a return. For instance, Rovio, creators of the very profitable Angry Birds game has developed many different video games you might not have heard of. Computer video games firms usually develop a whole lot of video games earlier than gaining one profitable game. It’s not all the time easy to identify the long run star and this can lead to probably wasted funds.
- Star products: Can be the market chief although require ongoing funding to maintain. They generate extra ROI than different product classes.
- Cash cow products: The easy rule right here is to ‘Milk these products as much as possible without killing the cow! Often mature, well-established products. The company Procter & Gamble which manufactures Pampers nappies to Lynx deodorants has often been described as a ‘cash cow company’.
Use the model as an outline of your products, fairly than detailed evaluation. If market share is small, use the ‘related market share’ axis is predicated in your rivals fairly than whole market.
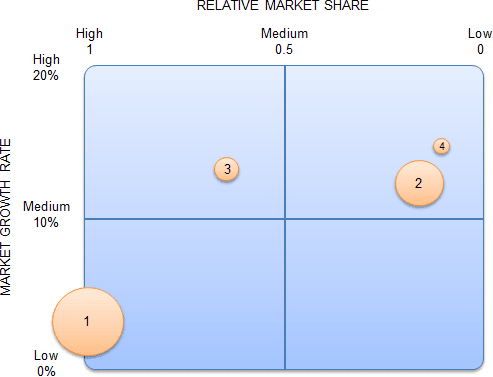
BCG Matrix
Boston Consulting Group (BCG) Matrix is a 4 celled matrix (a 2 * 2 matrix) developed by BCG, USA. It is probably the most famend company portfolio evaluation tool. It offers a graphic illustration for a corporation to look at totally different companies in it’s portfolio on the premise of their associated market share and business progress charges. It is a two dimensional evaluation on administration of SBU’s (Strategic Business Units). In different phrases, it’s a comparative evaluation of enterprise potential and the analysis of surroundings. According to this matrix, enterprise might be labeled as high or low in keeping with their business progress rate and relative market share.
Key Formula Reference
Relative Market Share = SBU Sales this year ÷ main rival’s sales this year
Market Growth Rate = (Industry sales this year – Industry Sales last year) ÷ Industry Sales last year × 100
The analysis requires that both measures be calculated for each SBU. The size of business energy, relative market share, will measure comparative benefit indicated by market dominance. The key concept underlying that is existence of an expertise curve and that market share is achieved as a result of overall value management.
BCG matrix has 4 cells, with the horizontal axis representing relative market share and the vertical axis denoting market progress rate.
The mid-point of relative market share is ready at 1.0. If all of the SBU’s are in similar business, the common progress rate of the business is used. While, if all of the SBU’s are positioned in several industries, then the mid-point is ready on the progress rate for the financial system. Resources are allotted to the enterprise items in keeping with their scenario on the grid. The 4 cells of this matrix have been known as as stars, money cows, query marks and canines. Each of those cells represents a selected type of enterprise.
 10 x 1 x 0.1 x 10 x 1 x 0.1 x |
Figure: BCG Matrix
The Four Quadrants Explained in Depth
- Stars- Stars symbolize enterprise items having giant market share in a quick rising business. They might generate money however due to quick rising market, stars require large investments to keep up their lead. Net money stream is normally modest. SBU’s positioned on this cell are engaging as they’re positioned in a sturdy business and these enterprise items are extremely aggressive within the business. If profitable, a star will turn into a money cow when the business matures.
- Cash Cows- Cash Cows represents enterprise items having a big market share in a mature, sluggish rising business. Cash cows require little funding and generate money that may be utilized for funding in different enterprise items. These SBU’s are the company’s key supply of money, and are particularly the core enterprise. They are the bottom of a corporation. These companies normally comply with stability methods. When money cows unfastened their enchantment and move in direction of deterioration, then a retrenchment coverage could also be pursued.
- Question Marks- Question marks symbolize enterprise items having low relative market share and positioned in a high progress business. They require large amount of money to keep up or acquire market share. They require consideration to find out if the enterprise will be viable. Question marks are typically new items and providers which have a good business potential. There isn’t any particular technique which will be adopted. If the agency thinks it has dominant market share, then it might probably undertake growth technique, else retrenchment technique will be adopted. Most companies begin as query marks because the company tries to enter a high progress market in which there’s already a market-share. If ignored, then query marks might turn into canines, whereas if large funding is made, then they’ve potential of changing into stars.
- Dogs- Dogs symbolize companies having weak market shares in low-growth markets. They neither generate money nor require large amount of money. Due to low market share, these enterprise items face value disadvantages. Generally retrenchment methods are adopted as a result of these corporations can acquire market share only on the expense of competitor’s/rival corporations. These enterprise corporations have weak market share due to high prices, poor high quality, ineffective advertising and marketing, and many others. Unless a canine has another strategic goal, it should be liquidated if there’s fewer prospects for it to achieve market share. Number of canines should be prevented and minimized in a corporation.
Pro Tip: The Nuance of Dog Products
While conventional wisdom suggests divesting dogs immediately, consider strategic exceptions. As the SAAB parts example illustrates, dogs can become profitable niche players when they serve a dedicated customer base with minimal ongoing investment. Evaluate each dog individually—some may be worth keeping as “cash dogs” that generate modest but reliable returns without requiring significant attention or resources.
Limitations of BCG Matrix
The BCG Matrix produces a framework for allocating resources amongst totally different enterprise items and makes it possible to match many enterprise items at a look. But BCG Matrix will not be free from limitations, such as-
- BCG matrix classifies companies as low and high, however typically companies will be medium additionally. Thus, the true nature of enterprise might not be mirrored.
- Market will not be clearly outlined on this model.
- High market share doesn’t all the time results in high income. There are high prices additionally concerned with high market share.
- Growth rate and relative market share should not the only indicators of profitability. This model ignores and overlooks different indicators of profitability.
- At occasions, canines might assist different companies in gaining aggressive benefit. They can earn much more than money cows generally.
- This four-celled approach is taken into account as to be too simplistic.
Warning: Misinterpreting Market Definition
The BCG Matrix is highly sensitive to how you define your market. A business unit that appears as a dog in the broad market definition may actually be a cash cow in its specific niche. For example, a luxury car manufacturer might have low relative market share in the overall automobile market but dominate the luxury segment. Always define markets strategically, not just broadly, to avoid misclassification and poor strategic decisions.
The progress share matrix was created in 1968 by BCG’s founder, Bruce Henderson. It was printed in one among BCG’s quick, provocative essays, known as Perspectives. At the peak of its success, the expansion share matrix was utilized by about half of all Fortune 500 firms; right this moment, it’s nonetheless central in enterprise faculty teachings on technique.
The progress share matrix is, put merely, a portfolio administration framework that helps firms determine methods to prioritize their totally different companies. It is a desk, break up into 4 quadrants, every with its personal distinctive image that represents a sure diploma of profitability: query marks, stars, pets (usually represented by a canine), and money cows. By assigning every enterprise to one among these 4 classes, executives might then determine the place to focus their resources and capital to generate probably the most worth, as well as the place to chop their losses.

The progress share matrix was built on the logic that market management ends in sustainable superior returns. Ultimately, the market chief obtains a self-reinforcing value benefit that rivals discover tough to duplicate. These high progress charges then sign which markets have probably the most progress potential. The matrix reveals two points that firms should contemplate when deciding the place to speculate—company competitiveness, and market attractiveness—with relative market share and progress rate because the underlying drivers of those factors. Each of the 4 quadrants represents a particular mixture of relative market share, and progress:
| Quadrant | Growth Rate | Market Share | Strategic Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cash Cows | Low | High | Milk profits to fund other units |
| Stars | High | High | Invest heavily for future potential |
| Question Marks | High | Low | Invest selectively or divest |
| Dogs | Low | Low | Liquidate, divest, or reposition |
As will be seen, product worth relies upon solely on whether or not or not a company is ready to get hold of a number one share of its market earlier than progress slows. All products will finally turn into both money cows or pets. Pets are pointless; they’re proof of failure to both get hold of a management place or to get out and lower the losses.
The growth-share matrix as soon as was used extensively, however has since pale from reputation as extra complete fashions have been developed. Some of its weaknesses are:
- Market progress rate is only one factor in business attractiveness, and relative market share is only one factor in aggressive benefit. The growth-share matrix overlooks many different factors in these two necessary determinants of profitability.
- The framework assumes that every enterprise unit is impartial of the others. In some cases, a enterprise unit that could be a “dog” could also be serving to different enterprise items acquire a aggressive benefit.
- The matrix relies upon closely upon the breadth of the definition of the market. A enterprise unit might dominate its small area of interest, however have very low market share within the overall business. In such a case, the definition of the market could make the difference between a canine and a money cow.
While its significance has diminished, the BCG matrix nonetheless can function a easy tool for viewing an organization’s enterprise portfolio at a look, and will function a place to begin for discussing useful resource allocation amongst strategic enterprise items.
The position of money stream within the BCG matrix
Understanding money stream is vital to taking advantage of the BCG matrix. In 1968, BCG founder Bruce Henderson noted that 4 guidelines are accountable for product money stream:
- Margins and money generated are a operate of market share. High margins and high market share go collectively.
- To develop, it’s worthwhile to spend money on your property. The added money required to carry share is a operate of progress charges.
- High market share have to be earned or purchased. Buying market share requires a further increment or funding.
- No product market can develop indefinitely. You must get your payoff from progress when the expansion slows; you lose your alternative if you happen to hesitate. The payoff is money that can’t be reinvested in that product.
That final level is much more necessary now than ever. The market strikes extra shortly now than it did 40 years in the past, and BCG has since printed really useful revisions to investigate and act on the matrix information. Maintaining a wholesome provide of query marks readies you to behave on the following pattern. Cash cows, conversely, should be milked effectively, as a result of they could fall out of favor – and profitability – extra shortly.
Pro Tip: Modern Cash Flow Dynamics
In today’s fast-moving markets, the lifecycle of products has compressed dramatically. What might have been a cash cow for decades in the past may now only generate stable returns for a few years before disruption. Regularly reassess your portfolio—quarterly rather than annually—and be prepared to move products between quadrants as market conditions shift. The cost of hesitation in digital markets is often permanent loss of competitive position.
You can discover extra methods on BCG’s web site. With a few tweaks, the matrix can be adapted to help companies drive the strategic experimentation required for success, even in unpredictable markets,” Martin stated. “The matrix needs to be applied with accelerated speed while balancing the investments between exploration in new segments and exploitation of established segments. In addition, the investments and divestments need to be managed rigorously while carefully measuring and monitoring the portfolio economics of experimentation.”
An actual-life BCG matrix instance
To perceive BCG-based progress, it may be worthwhile to take a look at a real-life BCG matrix example and then share the matrix with your team. A generally used BCG matrix instance is that of Coca-Cola, which owns many extra drinks than simply its titular model. In the Coca-Cola BCG matrix instance, Diet Coke and Minute Maid are query marks, as these names appeal to a modest viewers however nonetheless have loads of room to develop. Its bottled water manufacturers Kinley and Dasani are stars since they dominate the market in, respectively, Europe and the U.S. and present no indicators of slowing progress.
Its personal titular drink is a money cow because it experiences low progress regardless of its high market share, a categorization that is sensible given Coca-Cola’s ubiquity amongst mushy drinks. However, Coca-Cola can be a canine, as a result of laws in opposition to mushy drinks – to not point out public sentiment turning in opposition to them – has lessened soda gross sales. Coca-Cola’s real-life BCG matrix instance offers an necessary takeaway: Sometimes, a product can fall into multiple class.
Multiple Classifications: The Reality of Complex Portfolios
Coca-Cola’s example illustrates a crucial point about the BCG Matrix—products don’t always fit neatly into single quadrants. A brand may have cash cow characteristics in mature markets while simultaneously exhibiting dog characteristics in declining segments. Smart strategists analyze products at multiple levels: global brand positioning, regional performance, and category-specific dynamics. The matrix is a starting point for discussion, not a final verdict.
An different for an additional perspective
While a terrific tool, the BCG matrix is not for each enterprise. Some firms discover they do not have products in every quadrant, nor have they got regular motion of products among the many quadrants as they progress of their product life cycle. Some consultants advocate the usage of the GE/McKinsey matrix as a substitute, which affords extra categorization choices and measures products in keeping with enterprise unit energy and business attractiveness fairly than market share, the complexity of which may be exterior a person company’s control. Comparing the 2 fashions can reveal hidden insights that gasoline elevated progress in your company. Additional reporting by Max Freedman, Katherine Arline and Karina Fabian. Some supply interviews have been carried out for a previous model of this text.
GE/McKinsey Matrix vs. BCG Matrix
The GE/McKinsey Matrix offers a more nuanced approach with nine cells (3×3) rather than four. It evaluates business units on multiple factors:
- Industry Attractiveness: Market size, growth rate, competitive intensity, profitability, technological requirements, and regulatory environment
- Business Unit Strength: Market share, brand equity, distribution reach, innovation capability, cost structure, and management talent
This multidimensional approach provides richer strategic guidance but requires significantly more data and analysis. For small to medium businesses, the BCG Matrix’s simplicity often proves more practical and actionable.
Using the tool
Although BCG evaluation has misplaced its significance as a result of many limitations, it might probably nonetheless be a helpful tool if carried out by following these steps:
- Step 1. Choose the unit
- Step 2. Define the market
- Step 3. Calculate relative market share
- Step 4. Find out market progress rate
- Step 5. Draw the circles on a matrix
Step 1. Choose the unit.
BCG matrix can be utilized to investigate SBUs, separate manufacturers, products or a agency as a unit itself. Which unit shall be chosen will have an effect on the entire evaluation. Therefore, it’s important to outline the unit for which you’ll do the evaluation.
Step 2. Define the market.
Defining the market is among the most necessary issues to do on this evaluation. This is as a result of incorrectly outlined market might result in poor classification. For instance, if we might do the evaluation for the Daimler’s Mercedes-Benz car model within the passenger automobile market it will find yourself as a canine (it holds lower than 20% relative market share), however it will be a money cow within the luxurious car market. It is necessary to clearly outline the market to higher perceive agency’s portfolio place.
Relative market share will be calculated when it comes to revenues or market share. It is calculated by dividing your personal model’s market share (revenues) by the market share (or revenues) of your largest competitor in that business. For instance, in case your competitor’s market share in fridge’s business was 25% and your agency’s model market share was 10% in the identical yr, your relative market share can be only 0.4. Relative market share is given on x-axis. It’s top left nook is ready at 1, midpoint at 0.5 and top proper nook at 0 (see the instance below for this).

Step 4. Find out market progress rate.
The business progress rate will be present in business reviews, that are normally obtainable on-line without cost. It will also be calculated by common income progress of the main business corporations. Market progress rate is measured in share phrases. The midpoint of the y-axis is normally set at 10% progress rate, however this may fluctuate. Some industries develop for years however at common rate of 1 or 2% per yr. Therefore, when doing the evaluation you should discover out what progress rate is seen as important (midpoint) to separate money cows from stars and query marks from canines.
Step 5. Draw the circles on a matrix.
After calculating all of the measures, you should be capable to plot your manufacturers on the matrix. You should do that by drawing a circle for each model. The dimension of the circle should correspond to the proportion of enterprise income generated by that model.
BCG Matrix Implementation Checklist
- Define the strategic business units (SBUs) or products to analyze
- Clearly define the relevant market for each unit
- Gather competitor market share data
- Calculate relative market share for each unit
- Determine industry growth rate (set appropriate midpoint)
- Plot each unit with circle size proportional to revenue
- Analyze quadrant placement and portfolio balance
- Develop strategic recommendations for each quadrant
- Review and update quarterly or annually
Examples
Corporate ‘A’ BCG matrix
| Brand | Revenues | % of company revenues | Largest rival’s market share | Your model’s market share | Relative market share | Market progress rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brand 1 | $500,000 | 54% | 25% | 25% | 1 | 3% |
| Brand 2 | $350,000 | 38% | 30% | 5% | 0.17 | 12% |
| Brand 3 | $50,000 | 6% | 45% | 30% | 0.67 | 13% |
| Brand 4 | $20,000 | 2% | 10% | 1% | 0.1 | 15% |
This instance was created to indicate methods to take care of a relative market share greater than 100% and with unfavourable market progress.
Corporate ‘B’ BCG matrix
| Brand | Revenues | % of company revenues | Largest rival’s market share | Your model’s market share | Relative market share | Market progress rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brand 1 | $500,000 | 55% | 15% | 60% | 4.0 | 3% |
| Brand 2 | $350,000 | 31% | 30% | 5% | 0.17 | -15% |
| Brand 3 | $50,000 | 10% | 45% | 30% | 0.67 | -4% |
| Brand 4 | $20,000 | 4% | 10% | 1% | 0.1 | 8% |

Pro Tip: Handling Negative Growth Markets
When markets experience negative growth (contracting markets), the BCG matrix requires special interpretation. Products in negative growth markets may still be profitable even with low market share, as competitors exit and consolidate. In Company B’s example, Brand 3 shows negative growth but maintains strong relative market share—this might represent a niche defender position worth maintaining despite market contraction.
BCG Matrix in 2026

I suppose everybody is aware of what it’s the BCG Matrix, proper? For those that should not certain, it’s a matrix masking the product life cycle vs the utilization of money. You would possibly learn many explanations, however what about them from the Silicon Valley perspective.
QUESTION MARK – it’s technically the early stage product and something you launch and don’t have any concept in case your products are profitable or will thrive. Cash generation could be very low, you’ve got virtually no shoppers and no one is shopping for your product so your intention is to maneuver to Star; you possibly can technically sustain with the money utilization from the shopper who’s producing the money. This should occur in a short time as you can’t burn cash.
DOG – that is the time to rethink in case your enterprise is sensible or not. You hold burning cash, it’s not as high as in “Question mark” stage, however it’s high sufficient to appreciate that your company or products should not profitable. Rethink your technique; get issues proper and begin over once more. It’s most tough to shift to Star if the drive you had is gone and it’s worthwhile to refocus. You and your cash dried up!
STAR – that is probably the most constructive a part of the entrepreneurship. You would possibly get to the stage of your enterprise once you create one thing sensible and distinctive! Everyone will find it irresistible! Your company generates loads of money so you possibly can cowl the money utilization and develop your company as you need. You are in tune with the expansion of your company and you are able to do no matter you need, it’s the most pleasant a part of your endeavor!
COW – that is the perpetuum cellular the place the company retains producing money and you already know that there isn’t any further cent it’s worthwhile to spend to maintain that COW alive. The best technique to show COW stage, it’s to arrange the company as “owner absentee” and have a supervisor to run it. This half is nice once you run further firms or are beginning a brand new one. A company producing money is a superb alternative to start out one thing new as you don’t must put effort to generate money.
If I have a look at right this moment’s Silicon Valley firms none of them are pure COW, STAR, DOG or QUESTION MARK. Well, what I meant that right this moment’s Silicon Valleys firms (the profitable one, mid-size, and small dimension) are largely burning extra money that may be seen as STAR. It will nonetheless want money to generate further funds and on top of that, these firms obtain further capital to stop them from falling to the opposite segments. These firms is likely to be seen as SUPER-STAR – producing and spending money plus elevating extra cash to continue to grow and producing extra funds, which can finally be burned. This is right this moment’s BCG Matrix in Silicon Valley.
The SUPER-STAR Phenomenon
Modern growth companies, particularly in technology sectors, operate differently than the original BCG model envisioned. They simultaneously generate revenue, burn cash aggressively, and raise external capital—all while maintaining high growth rates. This “SUPER-STAR” quadrant represents a new reality where external funding supplements internal cash flow, enabling companies to remain in high-growth mode far longer than traditional models would suggest possible.
SUPER-STAR fundraising from traders as well as producing money stream from shoppers is the same as debt! Nobody is within the money COW! And lastly, why did I write this post? Well, we bought contacted by one of many BCG representatives! I can’t be extra excited, I don’t wish to say which of our firms, however it’s proof that we do “something” proper!
If the deal won’t undergo, the truth that we’ve been contacted by one of the prestigious firms on the planet speaks for itself! I keep in mind the day when my instructor of economics taught us about this matrix and now we’ve the possibility to work with this sensible company. I’ve the sensation that I want to leap on the airplane and discuss to them. I simply love these guys! They have been my STAR and COW all my life!
Strategic Applications for Small Businesses
While the BCG Matrix was designed for large corporations with diverse portfolios, entrepreneurs and small business owners can adapt its principles effectively:
- Product Line Prioritization: Use the matrix to decide which products deserve marketing budget, which should be maintained with minimal investment, and which should be discontinued.
- Time Allocation: Apply the framework to how you spend your time. Which activities are “stars” generating high growth? Which are “cash cows” providing steady returns with minimal effort?
- Customer Segmentation: Analyze customer segments through the BCG lens. Some customers may be “stars” (high growth potential, high current value), while others are “cash cows” (steady, reliable, low maintenance).
- Service Offerings: Evaluate your service portfolio. A consultant might have “star” services that are in high demand, “cash cow” services that provide steady income, and “dog” services that should be phased out.
Adapting BCG for Small Business Reality
Small businesses rarely have the data sophistication of large corporations, but they can still benefit from portfolio thinking. Instead of precise market share calculations, use qualitative assessments: Which products generate the most enthusiastic customer response? Which require disproportionate effort? Which provide reliable baseline revenue? The mental model matters more than mathematical precision.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
| Mistake | Consequence | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Defining markets too broadly | Misclassification of business units | Define markets at the level where competition actually occurs |
| Treating quadrants as permanent | Missing strategic inflection points | Review quarterly; markets and positions change |
| Ignoring interdependencies | Breaking valuable strategic relationships | Map how business units support each other |
| Over-relying on historical data | Past performance doesn’t guarantee future | Combine historical data with forward-looking analysis |
| Neglecting competitive dynamics | Strategies based on static assumptions | Incorporate competitor reactions into planning |
Warning: The Matrix is Not a Strategy
The BCG Matrix is a diagnostic tool, not a strategic plan. Identifying a product as a “dog” doesn’t automatically mean divestiture—it means further analysis is required. The matrix raises questions; it doesn’t provide answers. Always combine BCG analysis with deeper competitive, financial, and operational assessment before making strategic decisions.
Integrating BCG with Other Strategic Frameworks
The BCG Matrix works best when combined with complementary analytical tools:
- SWOT Analysis: Use SWOT to understand why products are in their current quadrants and what internal/external factors might move them.
- Porter’s Five Forces: Analyze industry structure to understand the competitive dynamics affecting each quadrant.
- Product Life Cycle: Map BCG positions to lifecycle stages for deeper insight into strategic requirements.
- Ansoff Matrix: Use growth strategies (market penetration, development, product development, diversification) to plan quadrant transitions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can the BCG Matrix be used for non-profit organizations?
Yes, with adaptation. Non-profits can evaluate programs and initiatives based on “impact growth rate” and “relative effectiveness” compared to other organizations serving similar needs. Cash cows might be fundraising events that generate reliable revenue; stars could be high-impact programs with growing demand; question marks might be experimental initiatives; dogs could be legacy programs with declining relevance.
How often should a company update its BCG Matrix?
For most industries, annual review is sufficient. However, in fast-moving sectors like technology or fashion, quarterly reviews may be necessary. The key is to review frequently enough to capture significant market changes but not so often that you’re reacting to noise rather than signals.
What’s the ideal portfolio balance according to BCG?
There’s no universal ideal—it depends on your industry, growth ambitions, and risk tolerance. Generally, companies want enough cash cows to fund stars and promising question marks, enough stars to ensure future cash cows, and minimal dogs. However, young companies may have mostly question marks, while mature companies may be cash cow heavy.
How do you handle products that span multiple quadrants?
Products often show different characteristics in different geographic markets or customer segments. In these cases, analyze at the segment level first, then develop composite strategies. Sometimes a product is a star in one region and a cash cow in another—this suggests different strategic approaches by region rather than a single global strategy.
Conclusion
The BCG Matrix, despite its age and acknowledged limitations, remains a valuable strategic tool for businesses of all sizes. Its enduring power lies in its simplicity—forcing executives to explicitly consider market position and growth potential when allocating resources. The visual nature of the matrix makes portfolio dynamics immediately understandable, facilitating strategic conversations across teams and leadership levels.
For modern businesses, the matrix requires adaptation. The SUPER-STAR concept captures today’s reality where external funding supplements internal cash flow, enabling extended high-growth periods. Market definitions must be carefully considered to avoid misclassification. And the matrix should always be used as a starting point for deeper analysis rather than a final decision-making tool.
Whether you’re managing a diverse corporate portfolio or simply trying to prioritize products in a small business, the BCG Matrix offers a framework for thinking strategically about where to invest, where to harvest, and where to exit. Combined with other analytical tools and updated regularly, it continues to provide value more than five decades after its creation.
For authoritative resources on strategic planning, consult the Boston Consulting Group’s official website, which offers original publications and updated thinking on portfolio management. For academic perspectives, Harvard Business Review maintains extensive archives on strategy frameworks. Small business owners can find practical applications through the U.S. Small Business Administration‘s planning resources.