Common WordPress Website Problems and Solutions
It may appear to be an excessive sum of money, but it is justifiable in light of the numerous chores that business owners must manage on a regular basis, such as maintaining current customers and developing several business profiles in prominent local directories. Furthermore, there are technical SEO difficulties that must be addressed, failing which the company’s online visibility may suffer. Businesses must discover and fix common on-site technical SEO problems with their websites to avoid losing clients and maintain business growth.
Links, structure, and content are the three basic sorts that might harm SEO. Although I believe that most readers understand the value of content structure and link development, there are many larger and poorly structured websites that have issues with URL construction. This can lead to a slew of other issues, including duplicate blog concerns. Here are some of the most common URL issues I’ve seen on various websites. If your website has one or more of these issues, look over these solutions and fix them as quickly as feasible.
1. Messy Code
Building a website requires a lot of coding, especially as the site grows in functionality and features. If your code is disorganised and sloppy, it can cause a slew of problems. It can influence not only how your website is supposed to work, but it can also affect search engines’ capacity to correctly index your site’s content, lowering your search ranks. The following are some examples of frequent website code issues:
Incorrect Robot.txt Files
Bots are used by search engines like Google to trawl through information on a website and index it for search ranking purposes. The robots exclusion protocol, often known as the robot.txt file, tells web crawlers and other web bots which parts of your site you don’t want processed or examined. Before crawling through the site, web crawlers will look for robot.txt files. If you employ robot.txt files poorly, web crawlers may not be able to read them properly, causing your entire site to be crawled and indexed. Here are some pointers on how to use robot.txt files correctly:
- To be found, robot.txt files must be placed in the top-level directory of your website.
- The names of robot.txt files must be all lower case, such as “robots.txt.”
- Each subdomain need its own robots.txt file.
- At the bottom of your robots.txt files, specify the location of any sitemaps linked with your domain.
- Because robot.txt files are publicly accessible, do not use them to mask confidential user information.
Lack Of A Sitemap File
A sitemap is a file that gives web crawlers information about all of your website’s pages, videos, and other assets. Creating a sitemap gives search engines a roadmap to your website, allowing them to index whatever you want them to. Sitemaps can also tell you what kind of content (such as images or videos) is on each page, when it was last updated, how frequently your pages change, and if you have any alternate language versions of your site. Web crawlers may miss parts of your pages if you don’t have a sitemap. If your content pages are isolated or not properly linked to one another, this can happen. In addition, newer sites may have fewer external links, making pages more difficult to find. In essence, a sitemap ensures that search engines receive the information they require about your website in order to effectively index and rank it.
Extreme Use Of Subfolders in URL Strings
A visitor who digs deep into your website may find up on a page with an excessive number of subfolders in the URL. This indicates that the URL is especially long and has many slashes. In many circumstances, the URL string is rather complicated, and you should simplify it. While a long URL string with subfolders won’t necessarily affect your site’s performance (nor will it hurt your page’s Google ranking), it will make it more difficult to modify your URL strings. It can also make it more difficult for visitors who wish to share your URL with others by copying and pasting it.
Multiple 404 Errors and Redirects
Broken links are the source of 404 errors. A broken link prevents the user from visiting the page you’re linking to, whether it’s an external or internal link, making their website experience more difficult. 404 redirects are pages that load to inform users that the page they are looking for is unavailable.
The page may be unavailable for a variety of reasons: it may no longer exist, it may have been modified, or the user may need to adjust their search. It’s critical to set up 404 redirects to let users know they’ve arrived at the correct page but that the link is broken. While 404 redirects are generally beneficial, having too many can negatively impact not only the user experience but also your search engine rankings. Fortunately, Google Analytics allows you to track 404 failures. As a result, you’ll be able to spot 404 errors early on and solve them before they cause more problems for your users.
No HTTPS Found
Always utilise HTTPS instead of HTTP when creating a website. This is especially true if you’re asking visitors for personal information like email addresses or credit card numbers. HTTPS is far more secure and helps to encrypt any data sent from a user to your website, guaranteeing that the data cannot be utilised if it is hacked and stolen.
Second, choose between using “www” and not using “www” when building your URL. Most users recognise a website address by the “.com” extension and rarely type “www” into the URL field. Using a “www” prefix, on the other hand, is theoretically correct and distinguishes your address from similar URLs for protocols like FTP or mail. Furthermore, if your top-level domain is a little less familiar or ambiguous, adding “www” removes any doubt that the URL is a web address. If you don’t use “www,” you’ll need to point your root domain DNS A-record to your web server’s IP address.
If you run into performance or availability concerns, this can become a little too rigid. Furthermore, whether or not the application uses the data, cookies established for domains that do not use “www” will be shared across all of your sub-domains. It’s also worth mentioning that “www” prefixes are required for many applications that convert text to links, such as word processors and email clients. In general, choose a web server configuration setting that allows visitors to use your domain with or without the “www” prefix to make a browser request.
2. Presence Of Broken Links
Broken links on your website are links that do not work, whether they are links that drive users to a page off your website or links that lead to a page on your website. When you click on a broken link, you’ll be brought to a 404 page, where you’ll get a message stating that the page you requested could not be located. Broken links can cause a number of problems. If a visitor clicks on a link and it does not take them to where they expect to go, they will be frustrated.
This has a negative impact on your website and brand. How can people trust the quality of your brand if you can’t keep your website up to date? Broken links can signal to Google and other search engines that your website isn’t kept up to date. Your search engine rankings may suffer as a result of this. When your rankings drop, your website’s exposure drops as well, resulting in fewer visits.
Canonicalization
The method of selecting a given URL as your preferred URL is known as canonicalization. Because there may be numerous slightly different URLs that direct readers to the same page, this is required. For instance, “domain.com” and “www.domain.com” or “https://domain.com?ref=twitter” are examples of domain names. Although all of these URLs may lead to the same page, web spiders may be confused as to which one to index because they are all different. It defines that URL as the one to index page content under by adding the rel=”canonical” tag to the head> element of your page. Canonicalization can also aid in the consolidation of redundant page link signals.
Non-Specific Page Titles
Page names and descriptions, as well as meta data, are critical for SERPs (search engine results pages). When your page appears on a SERP, the title and description convey information to the user about your page. They will be less inclined to click on the link if it does not have a title or description. You’ll want to double-check that your meta titles and descriptions adequately represent the information on the page to which the link leads. Make certain that each page has its own title. Many websites make the mistake of repeating titles over multiple pages. This will result in you missing out on prospective site traffic.
3. Poor Or Outdated Website Design
A website’s overall design must be both useful and appealing to the eye. After all, visitors will rate your website based on its appearance. Website design trends, on the other hand, shift frequently. This means that if you haven’t updated your site in a few years, it is most certainly outdated. The more out-of-date it appears, the less professional your brand appears. To follow modern website design concepts, you must update your site on a frequent basis. The following are some of the most prevalent problems that poor or outdated website designs have in common:
Improper Use Of Subdomain and Sub-Folders
A subdomain is a means to divide elements of your existing website. If you have a blog on your site, for example, the subdomain might be “blog.domain.com.” If you require distinct servers or software to run different areas of your website, you might want to explore using subdomains. If you don’t require this, subfolders are a better option. “www.domain.com/blog” is an example of a sub-folder for a blog. For the following reasons, using sub-folders is often the best method:
- Sub-folders allow your site to get crawled more often, which is helpful if you’re regularly adding new content.
- It’s easier for visitors to go between sections while on your site if you use sub-folders, such as from your product pages to your blog.
- It’s easier to use analytics tools to track website metrics since the data will be consolidated for your entire website.
Images That Lack Quality
Low resolution images are unacceptable. If your images are pixelated, it will reflect poorly on the quality of your brand. Only use high-quality images that are relevant to the content on the page you’re posting them on. Keep in mind that quality doesn’t just refer to resolution. Using unappealing images (such as pictures that are poorly lit or composed) will hurt your brand as well, no matter what resolution they’re in.
User Journey Is Perplexing
When someone comes to your website, you must make it obvious what you expect them to do. If they’re stuck on a page with no idea where to go next, it’s a sign that your site isn’t doing its job of guiding them through their user journey. This will make it more difficult for you to convert visitors. Internal linking, a simple navigation bar and search tool, and CTAs (calls-to-action) on each page are all essential for guiding your visitors. Examine indicators like high bounce rates to see whether your site has any difficulties with the user journey.
Forms That Are Both Required And Difficult
Forms are a great way to collect information from users and get permission to nurture leads. Visitors will be frustrated, though, if your forms are overly difficult or presented as required in order to complete specific actions. For example, a visitor can be annoyed if they add products to their shopping basket and proceed to checkout only to discover that they need to register to complete their purchase.
This will almost certainly lead to many potential customers abandoning their carts, especially if your forms include numerous phases. Make sure your forms are straightforward. Customers will be more likely to finish the form and check out if they only have to submit their names and shipping addresses. You can then give them the option to add more information to their profile at a later time when it is more convenient for them. Allowing social logins (for example, through Facebook) can also help to streamline the registration process. You should also consider offering guest checkout as an alternative to registration for individuals who don’t feel comfortable creating a profile just yet.
Making Use Of A Marketplace Theme
For your e-commerce page, avoid using pre-designed templates. This frequently leads to a misalignment between your brand image and your e-commerce platform, leading to customer uncertainty. For example, if the e-commerce page appears radically different from the rest of your site, customers may be unclear if they’re on the appropriate page and if they’re even on your site anymore.
4. Takes a long time to load
Visitors’ website experiences might be severely harmed by slow loading times. Few individuals have the patience to wait more than a few seconds for a page to load, especially given how rapidly other high-quality websites load. They can discover a site that will load if yours does not. Quickly general, most of your visitors will expect your page to load in under two seconds.
Expect to lose roughly 90% of visitors attempting to access that page if it takes more than three seconds to load. 79 percent of visitors won’t return to your website if it takes too long to load. If that wasn’t terrible enough, losing visitors due to poor loading times will result in a higher bounce rate. The bounce rate refers to the number of users that leave your page without engaging further. Your search engine rankings will suffer as a result of a high bounce rate.
Consult the manuals
Many factors can influence your loading speed, ranging from the inclusion of visual components (such as videos and animations) to the lack of mobile optimization, which can slow down loading times on mobile devices. You can use Google’s Page Speed Online tool to evaluate the speed of your pages to see if they are loading quickly enough. There are numerous resources available that will provide extensive instructions on how to enhance your page loading times.
Professionals should be hired
Hiring a professional is the simplest way to increase your website’s loading speed. A professional can help you reduce page load times in a variety of methods, including compressing all of your CSS, HTML, and JavaScript documents, and setting up CSS and JavaScript in external files. A specialist will be able to optimise your website’s backend to make it load faster.
5. Landing Pages That Aren’t Working
Landing pages are essential for converting leads. They assist in reinforcing the benefits of your offer, keeping leads motivated, and guiding them through the conversion process. If your landing pages are bad, your conversion rate is likely to be bad as well. The following are some of the most common mistakes people make when creating landing pages:
A General-Use Landing Page
Making a single landing page for all of your leads is about as effective as not having any landing pages at all. The content that brought your leads to the landing page in the first place must be relevant to the landing page. If a PPC ad offers a discount on a product, for example, the landing page should emphasise the product and the deal. If it’s merely a generic landing page, leads may be unsure whether they’ve arrived at the appropriate place. A high bounce rate may develop as a result of this. For each CTA, make sure you design a unique and relevant landing page.
Calls-to-Action that aren’t being answered
Although it is your CTAs that bring traffic to your landing pages, the landing pages themselves must also include CTAs. The last thing you want is for leads to be unclear of what they should do after arriving on your landing page. On each landing page you develop, include a CTA that clearly states the action you want your prospects to do.
Leaving Thank You Pages Blank
Make sure you appreciate a lead who converts through a landing page. Your leads will feel appreciated if you include a thank you page. This is crucial because once they submit a form, you’ll want to start creating your relationship with them so you can successfully nurture them through their buyer’s journey and beyond.
6. Incompatibility with mobile devices
According to the Pew Research Center, 77 percent of Americans have a smartphone in 2018. Only about 20% of folks in the United States use their smartphones to access the Internet. Furthermore, mobile phones account for 52.2 percent of all web traffic worldwide. This means that mobile devices will account for a considerable portion of your website traffic now and in the future.
Your website’s display on mobile devices will be affected if it isn’t mobile-friendly. You’ll lose a lot of prospective leads if your site doesn’t display properly, loads slowly (or at all), or is difficult to navigate on mobile devices. Furthermore, Google ranks mobile pages differently than desktop pages, implying that a lack of mobile optimization can hinder your potential to attract online traffic. While there are a variety of strategies to increase your site’s mobile friendliness, the most effective one is to adopt a responsive website design. Responsive design ensures that your site looks great on every screen, no matter how big or little it is.
7. There Is No SEO Optimization
Visitors will not appear out of nowhere. Your website must be adequately SEO-optimized (search engine optimization). Proper SEO optimization aids search engines in correctly identifying your content and can help you improve your SERP rankings, improving your visibility to your target audience and driving more visitors to your website. Your capacity to obtain new leads will be harmed if your SEO optimization is poor.
Content that is outdated or under-optimized
It’s no longer just about keywords; it’s about offering value by providing substantive, useful material to provide prospects with the information they seek. To show Google that you had a good experience, build trust and enhance website engagement metrics. SEO is more than just stuffing keywords into your material. It’s a lot more complicated than that.
While employing relevant keywords is beneficial, Google is more concerned with whether the material you’re giving is both relevant and of good quality. Google and other search engines use a variety of ranking signals to determine this, including how many external links your page has received from high-quality sources (external links indicate that your content is worthy of being linked to) and how much a visitor has engaged with the page (for example, by staying on the page for a long time, commenting on content, sharing the page on social media, or “liking” it on social media).
The more engaged visitors are on a page, the higher the chances of it ranking well. To develop trust and drive participation, focus on providing material that is useful, high-quality, and relevant to your target audience.
For a variety of reasons, the headers you employ to divide up your material are crucial. Visitors can skim your material and get a broad concept of what it’s about by using headers properly (including the appropriate use of keywords).
These headers also help search engines understand what your content is about and accurately index and rank your pages. Meta tags are also significant, as they serve a similar purpose to headers. While meta tags will not appear on your web pages, they will appear in the SERP. A meta tag is a fragment of text that provides a brief overview of the content contained on that specific page. It informs both search engines and users about the relevance of your webpage to the user’s query.
Problems with the Crawl Path
Every page of your site is crawled by search engine bots in order to properly index and rank it. They work by crawling outward from a variety of possible entry points (in the past, they would start from the homepage and work their way through, but they are more advanced now). Crawl path difficulties can occur if your site architecture is inadequate, which means that these bots may miss sites entirely.
Your search engine rankings may suffer as a result of this. There are a few things you can do to avoid crawl path difficulties. To begin, create a flat site hierarchy. This means that your homepage links to category pages, which in turn link to subcategory pages, which in turn lead to detail pages. Bots will find it much easier to crawl your site if you use a site map (and will make navigation more friendly for visitors as well). Faults in your sitemap, such as formatting errors or adding the wrong pages, will, nevertheless, cause issues. You should also keep an eye on your site for broken links, which might cause crawl route obstructions.
8. Overcrowding on the Home Page
Your homepage serves as an introduction to not just your website but also to your company. As a result, you must ensure that it makes a positive first impression on new visitors. Trying to offer too much information on a company’s site is one of the most common blunders. It becomes congested as a result of this. A busy site is tough to read and can make it difficult for visitors to find what they’re looking for.
Homepages that are identical
It’s not unusual to have multiple homepages. When you have numerous URLs leading to the same homepage, such as “www.domain.com” or “www.domain.com/index,” this happens. This not only confuses visitors, but it also hurts your rating because Google treats each URL separately. To avoid this, make sure your main homepage URL has a canonical tag.
The simplicity of navigating has a significant impact on the user experience of visitors. You have a problem if your homepage is so busy that a visitor can’t find the navigation bar. When someone visits on your homepage, your navigation bar should always be displayed. In your navigation bar, you should also avoid having too many categories and subfolders.
While being organised is beneficial, visitors will grow frustrated if your navigation bar contains a dozen alternatives with drop down menus that contain dozens of more possibilities. This will make finding what they’re looking for far more difficult for them. Your navigation menu should only contain the most significant links on your website.
Page Titles That Aren’t Specific
The titles of your pages show what content is available on each one. Non-specific page titles will not only confuse users (who will have difficulty finding certain pages or determining what page they are on for future reference), but they will also make it more difficult for search engines like Google to index your website. Use relevant keywords and keep the title under 70 characters when crafting specific page titles.
There are no contact details available.
If a visitor is considering contacting you, you don’t want to give them time to second-guess themselves. You also don’t want them to become so frustrated in their search for your contact information that they give up. Your contact information should be prominently displayed on your homepage. Most professional websites have a distinct contact page that visitors can access, as well as basic contact information (such as an email address and phone number) at the top of each page.
The existence of an entry page
The entry page is the first page a visitor sees when they come to your website. While the homepage is frequently the entry page, it is not always. If you’re running PPC (pay per click) advertisements, for example, create a distinct landing page for the ad. This entry page would be the landing page. You can utilise analytics tools to figure out which sites are used the most as entry pages. This might help you identify distinct entry pages so you can improve their capacity to nurture and convert leads by optimising them.
9. Issues with Security and Certification
Don’t think that just because you’re not a multibillion-dollar organisation, you’re immune to security dangers. Smaller businesses are frequently targeted by hackers these days since their security is typically lacking. An insecure website can cause major concerns – not only can it result in compliance issues, but it can also produce a public relations disaster, damaging your audience’s trust in your company.
Obtaining an SSL certificate (which results in the HTTPS protocol) will encrypt data sent between your users and your site, eliminating all of these security concerns. You should, however, be aware of the following frequent security concerns.
Email Address Revealed
You’ll almost certainly be gathering email addresses from your leads and customers, and you don’t want these addresses to be stolen and sold to strangers. Using HTTPS will help protect this information, but you should also take additional precautions, such as keeping your firewalls and anti-virus software up to date. There are a variety of other security technologies that you can use to not only increase the security of your site, but also to alert you to any vulnerabilities that need to be addressed and any breaches that need to be addressed before they cause too much damage.
You’ll also want to make sure that your email address isn’t visible. Your email address should be prominently displayed on your website so that potential customers may contact you. However, you don’t want spammers to collect your email address, resulting in a flood of unsolicited emails in your inbox. There are encryption techniques that may be used to post your email address on your website in a way that prevents it from being captured.
Copyright Legislation That Isn’t Up To Date
Copyrighting your website and displaying a copyright notice to assist deter infringement will help protect the content you create for your website from being used without your permission. However, because you’ll be continually upgrading your site, it’s critical that you renew the copyright on a regular basis, especially if it’s been a few years.
W3C Markup Validation Non-Compliance
The W3C(World Wide Web Consortium) is an international body that develops standards for the web. Be sure that your site remains in compliance with the standards established by the W3C by using their Markup Validation Service.
Delete everything after the domain name
Even if a specific page doesn’t seem to work, there’s a good chance the website still exists. Websites sometimes reorganize their content, so it’s possible the page is just in a different location. Try going to the site’s main page by deleting everything after the domain name:
- Select everything after the domain name. You can use this link if you’d like to practice.

- Press the Backspace or Delete key on your keyboard, then press Enter. The website should load correctly now.

- Use the site’s built-in search or navigation to try to find the page you want.
Solving more difficult problems
Sometimes it’s simply not possible to figure out how to fix a link. For example, if part of the link is missing, you may not know what the missing part was supposed to be. In these situations, you’ll need to try a backup plan. Here are a couple of methods we recommend:
- If someone sent you the link, ask if they can resend it.
- If you know the name (or a specific description) of the page, try Googling it. This works especially well for news articles; the exact same article may appear on multiple sites, which makes it even easier to find.
Of course, sometimes a page is taken down and there’s not much you can do about it. That’s just a part of life on the Internet—new content is created every day, and old content is eventually taken down.
If you absolutely need to find an old page, you can sometimes find it on the Wayback Machine, which periodically saves archived copies of billions of pages. However, this won’t work with all pages, and it only works if you have the original, correct URL of the page you’re trying to find.
10: What is a URL Shortener?
What is a URL shortener?

Although this URL (or web address) is 118 characters long, Twitter only allows 280-character postings. There aren’t enough characters left to mention anything about the link! Fortunately, URL shorteners are a simple solution. A URL shortener is an internet tool that converts your long URL into a new, shorter one that is easier to share. It’s not just for Twitter; it’s also for email, SMS messages, and any other occasion where a long URL would be too much to handle.
Let’s shorten a URL!
Even if you’ve never shortened a URL, it’s very easy. We’re going to use TinyURL, but the process will be similar when using other shortening services. The basic process is to copy the long URL into the URL shortener, and it will give you a shorter URL. The exact steps are below:
- Go to any website (you can use this link if you want). Websites with longer URLs are the best candidates for URL shortening, although any site will work.
- Select the URL in the address bar and copy it. You can use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+C (or Command+C on a Mac) to copy it.
- Go to TinyURL.com and paste the URL into the space provided, using the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+V (or Command+V).
- Click Make TinyURL.
- The shortened URL will appear. You can then copy the new URL and paste it wherever you want!
How it works
Basically, when the URL shortener gives you your shortened URL, it “remembers” the full address. When other users go to the shortened URL, they will be automatically redirected to the full address. The webpage will still exist at the longer URL—the shortened URL is simply a shortcut to make the link easier to manage.
So what can you do with a shortened URL?
URL shorteners aren’t just useful with Twitter. There are lots of situations where a shorter URL is more convenient:
- Emails: Long URLS can sometimes wrap to two or more lines, which makes them unwieldy.
- Resumes and cover letters: Shortened URLs can look a bit neater.
- Text messages: Most text messages have a limit of 160 characters, making short URLs essential.
- Phones: If you need to tell someone to go to a specific webpage, a shortened URL can save time and trouble.
Those are just a few examples, but URL shorteners can be used in any situation where a long URL would cause problems.
Other URL shorteners
We’ve focused on TinyURL, but there are many other URL shorteners out there. Below are just a few examples:
Some URL shorteners may require you to create a free account before using them, and the account may include additional features and perks. However, if you just need to shorten one or two URLs, we recommend using a service that doesn’t require an account. Some websites even have their own URL shorteners. A few of the most common ones are:
These specialized URL shorteners work the same as general-use ones, but they may be slightly more convenient to use because they are built into the site itself. For example, when you click the Share button on YouTube, it gives you a shortened version of the URL, starting with youtu.be (as shown below).
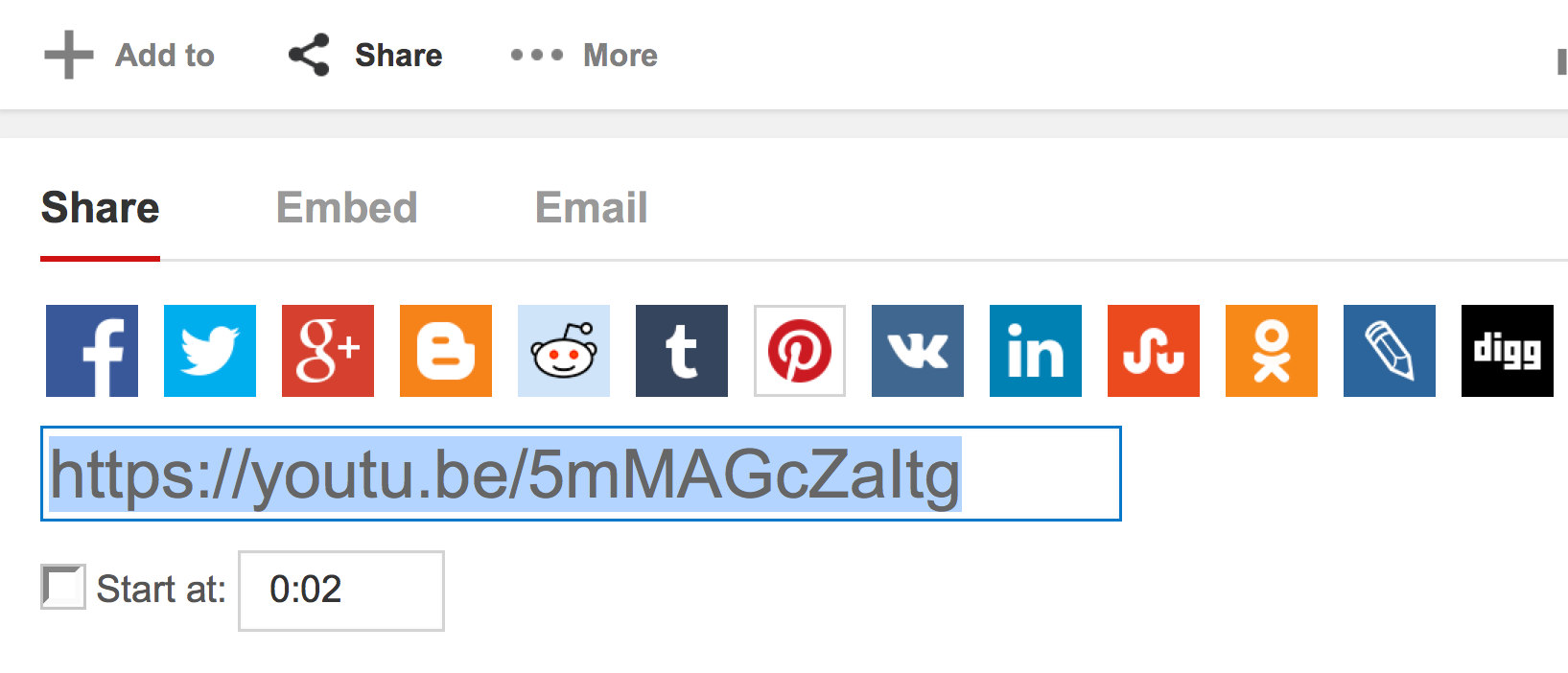
A word of caution
Shortened URLs may use a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, as well as numbers and other characters. If you ever need to manually copy the URL (whether typing, writing, or telling it to another person), it’s important to copy it exactly. For example, if you use a lowercase letter when it should be uppercase, it will go to a completely different website.
12: How Do I Check My Internet Speed?
How do I check my Internet speed?
Have you ever browsed the Internet at home and thought it was slower than normal? Or maybe your Internet just didn’t seem quite as fast as your service provider’s plan indicated? Luckily, it’s pretty easy to test your Internet speed and find out your exact specs. This can help you determine if things are slower than normal and pinpoint some problems.
Using a speed test website
There are a variety of websites that allow you to test your Internet speed for free, like SpeedTest or Google’s speed test (which can be accessed by searching for speed test). These sites will measure both your download speed and upload speed. They’ll also measure something called ping, which is the time it takes to send data to a server and back.

You’ll mostly be interested in your connection’s download speed, or how fast you’re able to pull data from other servers. This is typically measured in megabits per second (Mbps) and is a calculation of the speed at which your Internet is performing when surfing the Web and downloading files.
What’s considered a good speed?
For most basic Internet operations, such as regular web browsing or streaming music and video, a speed of roughly 10 Mbps should suffice. If you have a large family or a business where multiple people will be accessing the Internet at the same time, you may want to go for a plan with a faster download speed. If you plan on streaming high-definition video or live streaming video or music from your computer, a faster connection may be beneficial.
What can I do to improve my speed?
A slow Internet speed could be due to any number of factors. Below is a list of steps you can take to try and improve your speeds:
- Restart your modem and router. Over time, they may become clogged by errors or end up using too much processing power; a simple reset may help speed things up.
- Try using an Ethernet connection instead of Wi-Fi. Sometimes there can be wireless interference or an unreliable signal. By connecting via Ethernet, you may have a more stable connection with a higher speed.
- Close any programs or apps you’re not using. A lot of programs use the Internet. The less you have running the background, the faster you’ll be able to browse.
- Contact your Internet service provider (ISP). There may be a shortage or issue going on with the Internet in your area. The company will be able to inform you if this is case.
- If none of the above works and you continue to experience issues, you might want to look into changing your ISP. Other companies might simply have better speeds in your area. But make sure to do your research before switching over.
13: Website Speed
The speed of your website has a significant impact on its SERP ranking. Because a speedier website provides a better user experience, slower websites are penalised, causing them to fall in the rankings. If the server response time is more than 2 seconds, Google limits the number of crawlers delivered to your page. As a result, fewer pages will be indexed!
Google PageSpeed Insights, in a nutshell. This tool monitors and analyses your website’s performance on both desktop and mobile devices. For pages that are not properly optimised, alerts are sent out. The best thing is that PageSpeed Insights provides step-by-step instructions on how to fix the issue. WordPress users can also seek assistance from their hosting providers. It is suggested that you use a solid WordPress hosting service that has been thoroughly tested for uptime and speed (check out this list of 10 Best WordPress Hosting Services). Other than that, optimising your web page’s pictures, enabling browser caching, and minifying CSS and JavaScript may all help your website run faster.
14: Low Text-to-HTML Ratio
A low text-to-HTML ratio could indicate serious issues with your website’s technical SEO on-page. Low ratios could imply one of the following:
Due to filthy and bloated code, websites take a long time to load.
For search bots, hidden texts are a red indicator.
Flash, inline style, and Javascript are all over the place.
JavaScript is a terrific programming language, but it might slow down your site if you don’t know what you’re doing. Add pertinent on-page content when needed, relocate inline scripts to different files, and delete superfluous code to correct this. Here’s a great resource to get you started: 11 JavaScript Optimization Tips to Boost Website Loading and Rendering Speeds
15: Broken Links
One or two broken links on a website with hundreds of pages is to be expected and is scarcely an issue. Hundreds of broken connections, on the other hand, are a major setback because:
The user’s opinion of your website’s quality deteriorates.
Your crawl budget could be thrown out the window if you have broken links. When search bots encounter too many broken links, they redirect to other websites, leaving crucial pages on your site uncrawled and unindexed.
The page authority of your website is also harmed.
To find out which of your pages are returning 404 responses, go to Google Search Console and click on the “Crawl Errors” option under “Crawl.” Any 404 problems should be corrected as soon as possible to avoid bothering your visitors and redirecting them to other areas of your site – or off your site entirely!
16: Errors in Language Declarations
Language declarations are crucial for websites with a global audience so that the search engine can determine the language. This improves the user experience, especially for text-to-speech conversion, because translators can read the content in the correct dialect of the native language. Additionally, there are built-in international SEO and geo-location advantages.
Use the rel=”alternate” hreflang tag to define your website’s region specificity. Add a link element linking to the French version of the page at http://example.com.uk-fr to the head> section of http://sample.com/uk, as follows: link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”fr” href=”http://example.com/uk-fr” /> One of the most common mistakes made by websites is the use of incorrect language codes; to choose the correct code, use this HTML Language Code Reference list.
Remember that language declaration is a key part of the web page relevance score, which is crucial in and of itself for SEO. Another fault is return tag errors, which are caused by hreflang annotations that do not cross-reference one other. To find these problems, go to Google Search Console > International Targeting. These annotations must be verified by other pages; for example, if page A connects to page B, then B must link back to A.

17: Duplicate Content
Nearly 29% of the web, according to Raventools, has duplicate content. Make sure your website isn’t included in this list. Why? Not only can duplicated material hurt your rankings, but Google may also penalise your site. In fact, your site may lose its ability to rank in the SERPs entirely.
Analyze your site content with tools like Siteliner and Copyscape to confirm its originality. If duplicate material appears, choose one of the two alternatives listed below: In Google Webmasters, choose the URL version you want to use. Select “Site Settings” from the Settings menu on the upper right of the page, and then the appropriate URL format. When a site connects to a non-www version of your website and your preferred option is www, the linking URL will now be treated as the www version.
 There’s a higher risk of link sharing, website backlinking, and parameter tracking issues when multiple URLs contain the same content. Use the canonical tag to avoid this. The link to the actual resource will be found by any bot that comes across this tag. Each link to the duplicate page is regarded the same as if it were a link to the original page. As a result, the SEO value of such links is never lost. check out Unique SEO Process That Gets Results in 3 Key Phases with no contract SEO.
There’s a higher risk of link sharing, website backlinking, and parameter tracking issues when multiple URLs contain the same content. Use the canonical tag to avoid this. The link to the actual resource will be found by any bot that comes across this tag. Each link to the duplicate page is regarded the same as if it were a link to the original page. As a result, the SEO value of such links is never lost. check out Unique SEO Process That Gets Results in 3 Key Phases with no contract SEO.
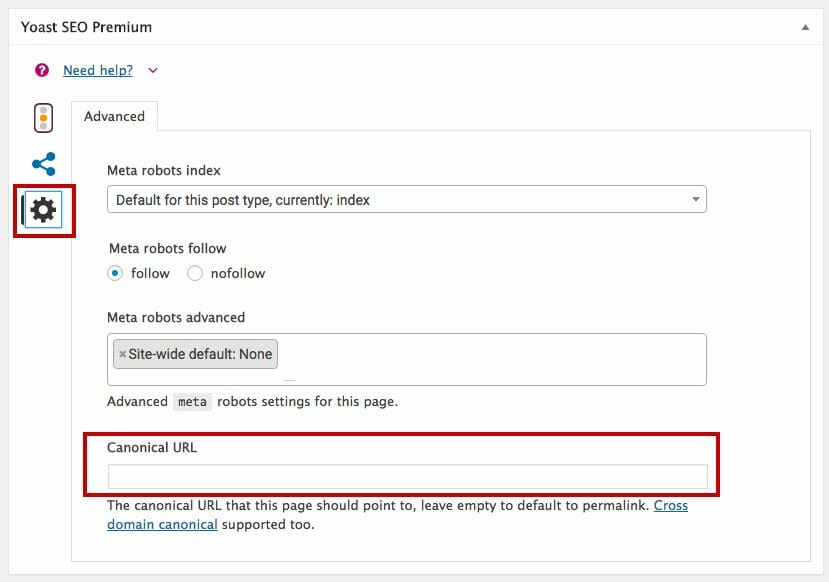
Add canonical tags to both the original and duplicate content by providing the following line of code: “link rel=”canonical” href=”https://yoursite.com.com/category/resource”/> Put the canonical tag in the meta description, which is at the bottom of the page for WordPress under “Yoast SEO Premium”:
18. Incompletely integrated
Does your company use a variety of platforms to promote itself? These days, all but the most traditional businesses have a presence on Facebook, as well as other social media platforms like Twitter and Instagram. A blog is also a fantastic way to increase traffic and interaction.
Do you, on the other hand, connect the dots? Is it possible for a user to access excellent reviews, recent Facebook posts, or a gallery of stunning photographs directly from your home page? You could be missing out on a lot of chances if there is a major disparity!
We would recommend a joined-up-thinking system for just about any organization for this reason (in fact, we launched our own basic platform called “Social Brilliance” to gather useful content!). Don’t forget to include your customers prominently in this as well; they are typically your best ambassadors and the ones who will most successfully spread the news about the positive things you do.
Conclusion – Common WordPress Website Problems and Solutions
We realize it’s been a long read, but we’re delighted you made it to the end and learned about 25 common website issues and how to fix them. If you need assistance with any of the difficulties we’ve listed on the website, or if you have a different issue, please email us or leave a comment below.
We hope you make the most of your website while avoiding all of the frequent and uncommon mistakes that may arise. There is no such thing as a perfect website. Having too many faults, on the other hand, can quickly escalate into major concerns that affect not only your site but your entire organization.
This paper summarizes the most common and high-priority difficulties that website owners experience in order to assist you comprehend all of the potential (hidden) concerns that you may be unaware of. Addressing these issues as soon as possible will help you enhance your site’s performance, increase traffic, give a good user experience, and leave a positive impression on your visitors.
It can assist you increase the quantity of leads and sales you create online from a business standpoint. All of this ensures that your website’s return on investment (ROI) is maximized. Managing a website is difficult labor that necessitates a great deal of talent, knowledge, and time. So, whether you need assistance with web development, design, or digital marketing, don’t be scared to seek out to specialists.
FAQ: 5 Common WordPress Errors
1. Error: White Screen of Death (WSOD)
Q: What is the White Screen of Death in WordPress?
A: The White Screen of Death (WSOD) is when your WordPress site shows a blank white page without any error message. This can happen due to several reasons, such as plugin or theme conflicts, memory limit exhaustion, or PHP errors.
Q: How can I fix the White Screen of Death?
A: Here are a few steps to resolve the WSOD:
- Disable Plugins: Use FTP to access your WordPress files. Navigate to the
wp-content/pluginsdirectory and rename the plugins folder toplugins_old. Check your site to see if it loads. If it does, rename the folder back topluginsand deactivate plugins one by one to identify the culprit. - Switch to a Default Theme: Rename your active theme folder in
wp-content/themesto force WordPress to revert to a default theme. - Increase Memory Limit: Add
define('WP_MEMORY_LIMIT', '256M');to yourwp-config.phpfile to increase the PHP memory limit. - Enable Debugging: Add
define('WP_DEBUG', true);towp-config.phpto display errors that can help identify the problem.
2. Error: 500 Internal Server Error
Q: What causes the 500 Internal Server Error in WordPress?
A: The 500 Internal Server Error is a generic error message indicating something went wrong on the server. Common causes include corrupted .htaccess files, exhausted PHP memory limit, or incompatible plugins/themes.
Q: Why do I see a 404 error on my WordPress site?
A: A 404 error typically occurs when the server cannot find the requested page. This can happen if permalinks are not set up correctly or if a page/post has been deleted without updating links.
A: To resolve this issue:
- Delete .maintenance File: Use FTP to access your WordPress root directory and delete the
.maintenancefile.
5. Error: Connection Timed Out
Q: What causes the Connection Timed Out error in WordPress?
A: This error usually occurs when the server is overloaded, your site is trying to handle too many processes, or your hosting server doesn’t have enough resources.
By following these steps, you can troubleshoot and fix these common WordPress errors to ensure your site runs smoothly. If the issue persists, consider reaching out to a professional or your hosting provider for further assistance.






